Page 138 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 138
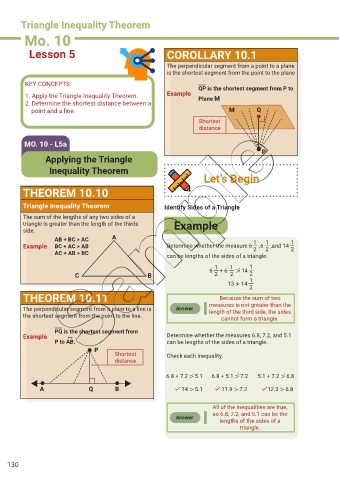
Triangle Inequality Theorem
Mo. 10
Lesson 5 COROLLARY 10.1
The perpendicular segment from a point to a plane
is the shortest segment from the point to the plane
KEY CONCEPTS: QP is the shortest segment from P to
1. Apply the Triangle Inequality Theorem. Example Plane M
2. Determine the shortest distance between a
point and a line. M Q
Shortest
distance
MO. 10 - L5a
P
Applying the Triangle
Inequality Theorem
Let’s Begin
THEOREM 10.10
Triangle Inequality Theorem Identify Sides of a Triangle
The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a
triangle is greater than the length of the thirds Example
side.
AB + BC > AC A
1
1
Example BC + AC > AB Determine whether the measure 6 ,6 ,and 14 1
2
2
2
AC + AB > BC can be lengths of the sides of a triangle.
1 1 1
6 + 6 ⩼ 14
C B 2 2 2
13 ≯ 14 1
2
THEOREM 10.11 Because the sum of two
The perpendicular segment from a point to a line is Answer measures is not greater than the
length of the third side, the sides
the shortest segment from the point to the line. cannot form a triangle.
PQ is the shortest segment from
Example ↔ Determine whether the measures 6.8, 7.2, and 5.1
P to AB. can be lengths of the sides of a triangle.
P
Shortest Check each inequality.
distance
6.8 + 7.2 ⩼ 5.1 6.8 + 5.1 ⩼ 7.2 5.1 + 7.2 ⩼ 6.8
A Q B 14 > 5.1 11.9 > 7.2 12.3 > 6.8
All of the inequalities are true,
so 6.8, 7.2, and 5.1 can be the
Answer
lengths of the sides of a
triangle.
130