Page 169 - Math Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 169
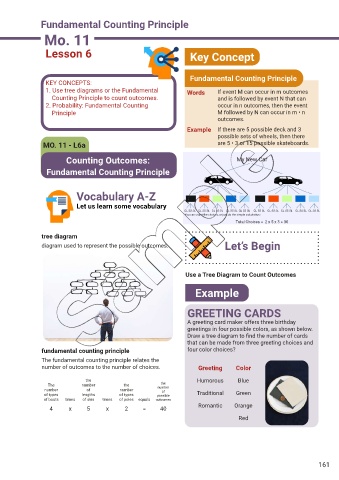
Fundamental Counting Principle
Mo. 11
Lesson 6 Key Concept
Fundamental Counting Principle
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. Use tree diagrams or the Fundamental Words If event M can occur in m outcomes
Counting Principle to count outcomes. and is followed by event N that can
2. Probability: Fundamental Counting occur in n outcomes, then the event
Principle M followed by N can occur in m • n
outcomes.
Example If there are 5 possible deck and 3
possible sets of wheels, then there
MO. 11 - L6a are 5 • 3 or 15 possible skateboards.
Counting Outcomes: My New Car
Fundamental Counting Principle
Vocabulary A-Z
Let us learn some vocabulary
GL SS SL GL SS SL GL SS SL GL SS SL GL SS SL GL SS SL GL SS SL GL SS SL GL SS SL GL SS SL
You can count the choices, or just do the simple calculation:
Total Choices = 2 x 5 x 3 = 30
tree diagram
diagram used to represent the possible outcomes. Let’s Begin
Use a Tree Diagram to Count Outcomes
Example
GREETING CARDS
A greeting card maker offers three birthday
greetings in four possible colors, as shown below.
Draw a tree diagram to f nd the number of cards
that can be made from three greeting choices and
fundamental counting principle four color choices?
The fundamental counting principle relates the
number of outcomes to the number of choices. Greeting Color
the Humorous Blue
the
The number the number
number of number of
of types lengths of types possible Traditional Green
of boots times of skis times of poles equals outcomes
Romantic Orange
4 x 5 x 2 = 40
Red
161