Page 117 - Math Course 2 (Book 1)
P. 117
Factoring: Polynomials
Let’s Begin
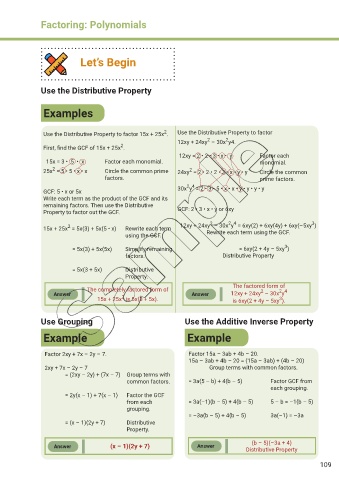
Use the Distributive Property
Examples
2
Use the Distributive Property to factor 15x + 25x . Use the Distributive Property to factor
2
2
12xy + 24xy – 30x y4.
2
First, f nd the GCF of 15x + 25x .
12xy = 2 • 2 • 3 • x • y Factor each
15x = 3 • 5 • x Factor each monomial. monomial.
2
2
25x = 5 • 5 • x • x Circle the common prime 24xy = 2 • 2 • 2 • 3 • x • y • y Circle the common
factors. prime factors.
2 4
30x y = 2 • 3 • 5 • x • x • y • y • y • y
GCF: 5 • x or 5x
Write each term as the product of the GCF and its
remaining factors. Then use the Distributive
Property to factor out the GCF. GCF: 2 • 3 • x • y or 6xy
3
2
2 4
2
15x + 25x = 5x(3) + 5x(5 • x) Rewrite each term 12xy + 24xy – 30x y = 6xy(2) + 6xy(4y) + 6xy(–5xy )
using the GCF. Rewrite each term using the GCF.
3
= 5x(3) + 5x(5x) Simplify remaining = 6xy(2 + 4y – 5xy )
factors. Distributive Property
= 5x(3 + 5x) Distributive
Property.
The factored form of
The completely factored form of 2 2 4
Answer Answer 12xy + 24xy – 30x y
2
15x + 25x is 5x(3 + 5x). is 6xy(2 + 4y – 5xy ).
3
Use Grouping Use the Additive Inverse Property
Example Example
Factor 2xy + 7x – 2y – 7. Factor 15a – 3ab + 4b – 20.
15a – 3ab + 4b – 20 = (15a – 3ab) + (4b – 20)
2xy + 7x – 2y – 7 Group terms with common factors.
= (2xy – 2y) + (7x – 7) Group terms with
common factors. = 3a(5 – b) + 4(b – 5) Factor GCF from
each grouping.
= 2y(x – 1) + 7(x – 1) Factor the GCF
from each = 3a(–1)(b – 5) + 4(b – 5) 5 – b = –1(b – 5)
grouping.
= –3a(b – 5) + 4(b – 5) 3a(–1) = –3a
= (x – 1)(2y + 7) Distributive
Property.
(b – 5)(–3a + 4)
Answer (x – 1)(2y + 7) Answer
Distributive Property
109