Page 62 - Math Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 62
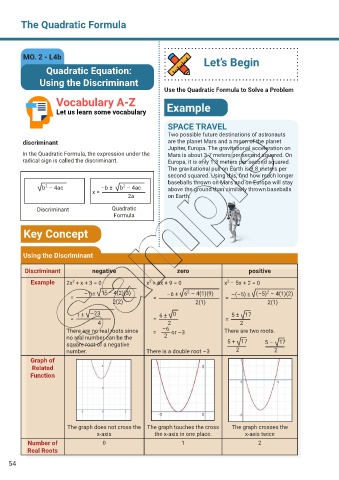
The Quadratic Formula
MO. 2 - L4b Let’s Begin
Quadratic Equation:
Using the Discriminant
Use the Quadratic Formula to Solve a Problem
Vocabulary A-Z
Let us learn some vocabulary Example
SPACE TRAVEL
Two possible future destinations of astronauts
discriminant are the planet Mars and a moon of the planet
Jupiter, Europa. The gravitational acceleration on
In the Quadratic Formula, the expression under the Mars is about 3.7 meters per second squared. On
radical sign is called the discriminant. Europa, it is only 1.3 meters per second squared.
The gravitational pull on Earth is 9.8 meters per
second squared. Using this, find how much longer
baseballs thrown on Mars and on Europa will stay
2
2
b – 4ac –b ± b – 4ac above the ground than similarly thrown baseballs
x =
2a on Earth.
Discriminant Quadratic
Formula
Key Concept
Using the Discriminant
Discriminant negative zero positive
Example 2x + x + 3 = 0 x + 6x + 9 = 0 x – 5x + 2 = 0
2
2
2
2
2
2
–1 ± 1 – 4(2)(3) –6 ± 6 – 4(1)(9) –(–5) ± (–5) – 4(1)(2)
= = =
2(2) 2(1) 2(1)
1 ± –23 6 ± 0 5 ± 17
= = =
4 2 2
There are no real roots since = –6 or –3 There are two roots.
no real number can be the 2 5 + 17
square root of a negative 5 – 17
number. There is a double root –3 2 2
Graph of
Related
Function
The graph does not cross the The graph touches the cross The graph crosses the
x-axis the x-axis in one place. x-axis twice
Number of 0 1 2
Real Roots
54