Page 163 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 163
Circles: Arcs and Chords
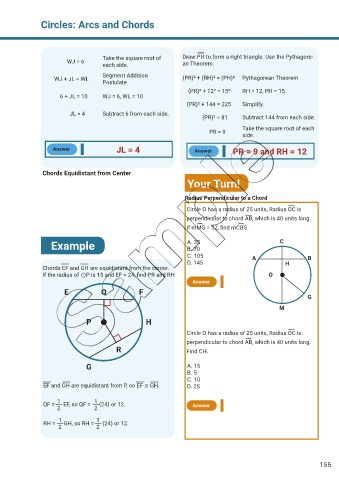
Take the square root of Draw PH to form a right triangle. Use the Pythagore-
WJ = 6
each side. an Theorem.
Segment Addition
WJ + JL = WL (PR)² + (RH)² = (PH)² Pythagorean Theorem
Postulate
(PR)² + 12² = 15² RH = 12, PH = 15
6 + JL = 10 WJ = 6, WL = 10
(PR)² + 144 = 225 Simplify.
JL = 4 Subtract 6 from each side.
(PR)² = 81 Subtract 144 from each side.
Take the square root of each
PR = 9
side.
Answer JL = 4 Answer PR = 9 and RH = 12
Chords Equidistant from Center
Your Turn!
Radius Perpendicular to a Chord
Circle O has a radius of 25 units, Radius OC is
perpendicular to chord AB, which is 40 units long.
If mMG = 32, find mCBG.
Example A. 35 C
B. 70
C. 105 A B
D. 145 H
Chords EF and GH are equidistant from the center.
If the radius of ⊙P is 15 and EF = 24, find PR and RH O
Answer
E Q F
G
M
P H
Circle O has a radius of 25 units, Radius OC is
perpendicular to chord AB, which is 40 units long.
R Find CH.
G A. 15
B. 5
C. 10
EF and GH are equidistant from P, so EF ≅ GH. D. 25
1
1
QF = EF, so QF = (24) or 12. Answer
2 2
1
1
RH = GH, so RH = (24) or 12.
2 2
155