Page 173 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 173
Circles: Equations
Mo. 11
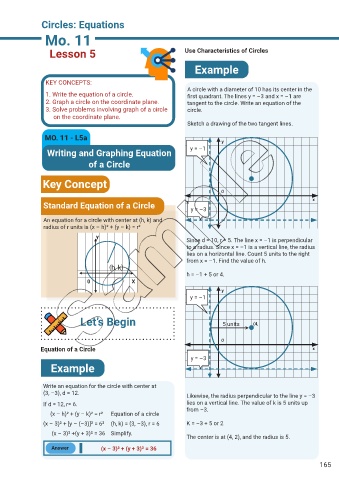
Lesson 5 Use Characteristics of Circles
Example
KEY CONCEPTS:
A circle with a diameter of 10 has its center in the
1. Write the equation of a circle. first quadrant. The lines y = –3 and x = –1 are
2. Graph a circle on the coordinate plane. tangent to the circle. Write an equation of the
3. Solve problems involving graph of a circle circle.
on the coordinate plane.
Sketch a drawing of the two tangent lines.
MO. 11 - L5a
y
Writing and Graphing Equation y = –1
of a Circle
Key Concept
O
x
Standard Equation of a Circle y = –3
An equation for a circle with center at (h, k) and
radius of r units is (x – h)² + (y – k) = r²
y
Since d = 10, r = 5. The line x = –1 is perpendicular
to a radius. Since x = –1 is a vertical line, the radius
lies on a horizontal line. Count 5 units to the right
from x = –1. Find the value of h.
(h, k)
h = –1 + 5 or 4.
0 X
y
y = –1
Let’s Begin 5 units (4,
O
Equation of a Circle x
y = –3
Example
Write an equation for the circle with center at
(3, –3), d = 12.
Likewise, the radius perpendicular to the line y = –3
If d = 12, r= 6. lies on a vertical line. The value of k is 5 units up
from –3.
(x – h)² + (y – k)² = r² Equation of a circle
(x – 3)² + [y – (–3)]² = 6² (h, k) = (3, –3), r = 6 K = –3 + 5 or 2
(x – 3)² +(y + 3)² = 36 Simplify.
The center is at (4, 2), and the radius is 5.
Answer (x – 3)² + (y + 3)² = 36
165