Page 42 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 42
Mo2-L1a: What are Living Things?
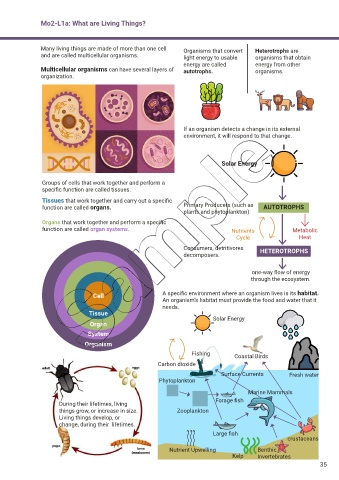
Many living things are made of more than one cell Organisms that convert Heterotrophs are
and are called multicellular organisms. light energy to usable organisms that obtain
energy are called energy from other
Multicellular organisms can have several layers of autotrophs. organisms.
organization.
If an organism detects a change in its external
environment, it will respond to that change.
Solar Energy
Groups of cells that work together and perform a
specific function are called tissues.
Tissues that work together and carry out a specific
function are called organs. Primary Producers (such as AUTOTROPHS
plants and phytoplankton)
Organs that work together and perform a specific
function are called organ systems. Nutrients Metabolic
Cycle Heat
Consumers, detritivores HETEROTROPHS
decomposers.
one-way flow of energy
through the ecosystem.
Cell A specific environment where an organism lives is its habitat.
An organism’s habitat must provide the food and water that it
needs.
Tissue
Solar Energy
Organ
System
Organism
Fishing Coastal Birds
Carbon dioxide
Surface Currents Fresh water
Phytoplankton
Marine Mammals
Forage fish
During their lifetimes, living
things grow, or increase in size. Zooplankton
Living things develop, or
change, during their lifetimes.
Large fish
crustaceans
Nutrient Upwelling Benthic
Kelp Invertebrates
35