Page 122 - Science Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 122
Mo9-L4a: How is Energy Transferred in the Atmosphere?
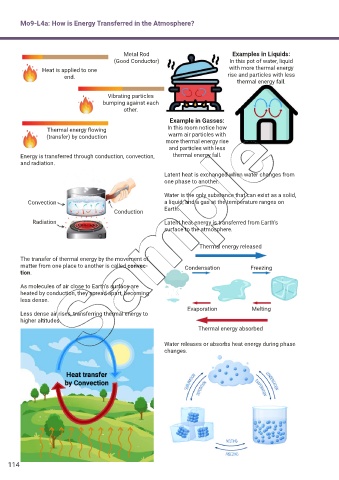
Metal Rod Examples in Liquids:
(Good Conductor) In this pot of water, liquid
Heat is applied to one with more thermal energy
end. rise and particles with less
thermal energy fall.
Vibrating particles
bumping against each
other.
Example in Gasses:
Thermal energy f owing In this room notice how
(transfer) by conduction warm air particles with
more thermal energy rise
and particles with less
Energy is transferred through conduction, convection, thermal energy fall.
and radiation.
Latent heat is exchanged when water changes from
one phase to another.
Water is the only substance that can exist as a solid,
Convection a liquid, and a gas at the temperature ranges on
Conduction Earth.
Radiation Latent heat energy is transferred from Earth’s
surface to the atmosphere.
Thermal energy released
The transfer of thermal energy by the movement of
matter from one place to another is called convec- Condensation Freezing
tion.
As molecules of air close to Earth’s surface are
heated by conduction, they spread apart, becoming
less dense.
Evaporation Melting
Less dense air rises, transferring thermal energy to
higher altitudes.
Thermal energy absorbed
Water releases or absorbs heat energy during phase
changes.
114