Page 25 - Science Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 25
Newton’s Second Law of Motion Mo8-L3a: What is Newton’s Second Law
Lesson 3 of Motion?
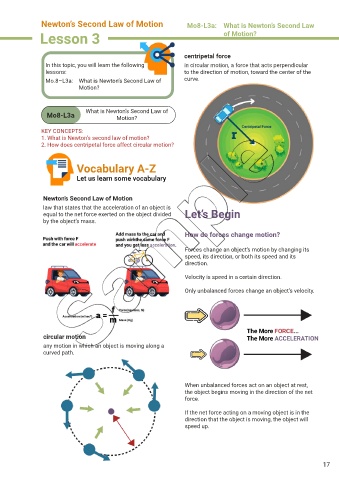
centripetal force
In this topic, you will learn the following in circular motion, a force that acts perpendicular
lessons: to the direction of motion, toward the center of the
Mo.8–L3a: What is Newton’s Second Law of curve.
Motion?
What is Newton’s Second Law of
Mo8-L3a Motion?
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. What is Newton’s second law of motion?
2. How does centripetal force affect circular motion?
Vocabulary A-Z
Let us learn some vocabulary
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
law that states that the acceleration of an object is
equal to the net force exerted on the object divided Let’s Begin
by the object’s mass.
How do forces change motion?
Forces change an object’s motion by changing its
speed, its direction, or both its speed and its
direction.
Velocity is speed in a certain direction.
Only unbalanced forces change an object’s velocity.
circular motion
any motion in which an object is moving along a
curved path.
When unbalanced forces act on an object at rest,
the object begins moving in the direction of the net
force.
If the net force acting on a moving object is in the
direction that the object is moving, the object will
speed up.
17