Page 84 - Science Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 84
Mo10-L2a: What is the Carbon Cycle?
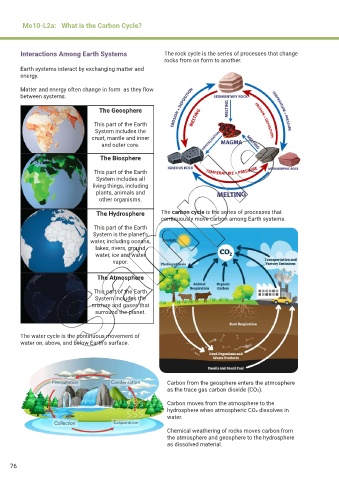
Interactions Among Earth Systems The rock cycle is the series of processes that change
rocks from on form to another.
Earth systems interact by exchanging matter and
energy.
Matter and energy often change in form as they f ow
between systems.
The Geosphere
This part of the Earth
System includes the
crust, mantle and inner
and outer core.
The Biosphere
This part of the Earth
System includes all
living things, including
plants, animals and
other organisms.
The Hydrosphere The carbon cycle is the series of processes that
continuously move carbon among Earth systems.
This part of the Earth
System is the planet’s
water, including oceans,
lakes, rivers, ground
water, ice and water
vapor.
The Atmosphere
This part of the Earth
System includes the
mixture and gases that
surround the planet.
The water cycle is the continuous movement of
water on, above, and below Earth’s surface.
Carbon from the geosphere enters the atmosphere
as the trace gas carbon dioxide (CO2).
Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the
hydrosphere when atmospheric CO2 dissolves in
water.
Chemical weathering of rocks moves carbon from
the atmosphere and geosphere to the hydrosphere
as dissolved material.
76