Page 192 - Science Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 192
Mo5-L1b: What did Mendel Discover About Heredity?
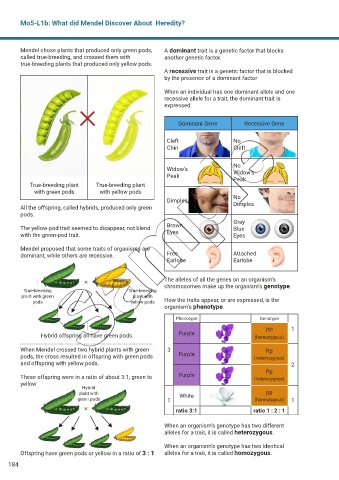
Mendel chose plants that produced only green pods, A dominant trait is a genetic factor that blocks
called true-breeding, and crossed them with another genetic factor.
true-breeding plants that produced only yellow pods.
A recessive trait is a genetic factor that is blocked
by the presence of a dominant factor
When an individual has one dominant allele and one
recessive allele for a trait, the dominant trait is
expressed.
Dominant Gene Recessive Gene
Cleft No
Chin Cleft
No
Widow’s Widow’s
Peak Peak
True-breeding plant True-breeding plant
with green pods with yellow pods
Dimples No
Dimples
All the offspring, called hybrids, produced only green
pods.
Gray
The yellow-pod trait seemed to disappear, not blend Brown Blue
with the green-pod trait. Eyes Eyes
Mendel proposed that some traits of organisms are
dominant, while others are recessive. Free Attached
Earlobe Earlobe
The alleles of all the genes on an organism’s
chromosomes make up the organism’s genotype.
True-breeding True-breeding
plant with green plant with
pods yellow pods How the traits appear, or are expressed, is the
organism’s phenotype.
Phenotype Genotype
PP 1
Hybrid offspring all have green pods. Purple (homozygous)
When Mendel crossed two hybrid plants with green 3 Pp
pods, the cross resulted in offspring with green pods Purple (heterozygous)
and offspring with yellow pods. 2
Pp
These offspring were in a ratio of about 3:1, green to Purple (heterozygous)
yellow
Hybrid
plant with White pp
green pods 1 (homozygous) 1
ratio 3:1 ratio 1 : 2 : 1
When an organism’s genotype has two different
alleles for a trait, it is called heterozygous.
When an organism’s genotype has two identical
Offspring have green pods or yellow in a ratio of 3 : 1 alleles for a trait, it is called homozygous.
184