Page 50 - Science Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 50
Mo2-L1b: How Do Living Organisms Interact?
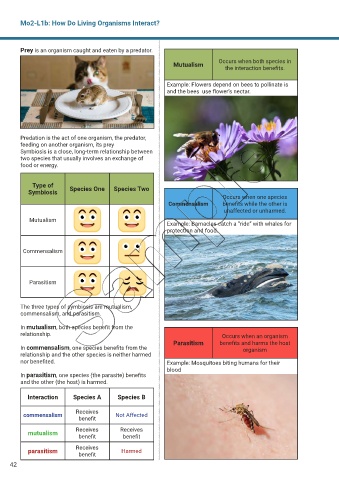
Prey is an organism caught and eaten by a predator.
Occurs when both species in
Mutualism
the interaction benefits.
Example: Flowers depend on bees to pollinate is
and the bees use flower’s nectar.
Predation is the act of one organism, the predator,
feeding on another organism, its prey
Symbiosis is a close, long-term relationship between
two species that usually involves an exchange of
food or energy.
Type of
Symbiosis Species One Species Two
Occurs when one species
Commensalism benefits while the other is
unaffected or unharmed.
Mutualism
Example: Barnacles catch a “ride“ with whales for
protection and food.
Commensalism
Parasitism
The three types of symbiosis are mutualism,
commensalism, and parasitism.
In mutualism, both species benefit from the
relationship. Occurs when an organism
Parasitism benefits and harms the host
In commensalism, one species benefits from the organism
relationship and the other species is neither harmed
nor benefited. Example: Mosquitoes biting humans for their
blood
In parasitism, one species (the parasite) benefits
and the other (the host) is harmed.
Interaction Species A Species B
Receives
commensalism Not Affected
benefit
Receives Receives
mutualism
benefit benefit
parasitism Receives Harmed
benefit
42