Page 48 - Science Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 48
Mo10-L1b: What are the Properties of Waves?
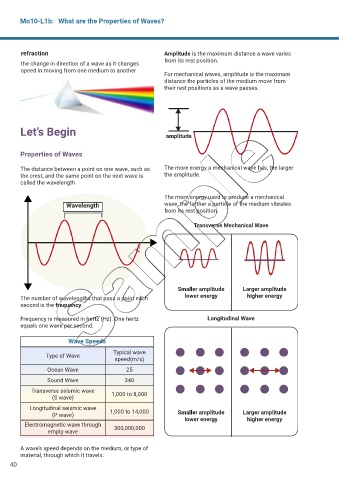
refraction Amplitude is the maximum distance a wave varies
from its rest position.
the change in direction of a wave as it changes
speed in moving from one medium to another
For mechanical waves, amplitude is the maximum
distance the particles of the medium move from
their rest positions as a wave passes.
Let’s Begin amplitude
Properties of Waves
The distance between a point on one wave, such as The more energy a mechanical wave has, the larger
the crest, and the same point on the next wave is the amplitude.
called the wavelength
The more energy used to produce a mechanical
Wavelength wave, the farther a particle of the medium vibrates
from its rest position.
Transverse Mechanical Wave
Smaller amplitude Larger amplitude
The number of wavelengths that pass a point each lower energy higher energy
second is the frequency.
Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz). One hertz Longitudinal Wave
equals one wave per second.
Wave Speeds
Typical wave
Type of Wave
speed(m/s)
Ocean Wave 25
Sound Wave 340
Transverse seismic wave 1,000 to 8,000
(S wave)
Longitudinal seismic wave 1,000 to 14,000
(P wave) Smaller amplitude Larger amplitude
lower energy higher energy
Electromagnetic wave through 300,000,000
empty wave
A wave’s speed depends on the medium, or type of
material, through which it travels.
40