Page 10 - Math Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 10
Properties of Identity and Equality
Mo. 7
Lesson 1
Let’s Begin
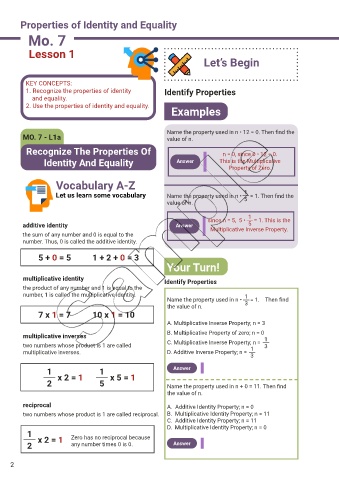
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. Recognize the properties of identity Identify Properties
and equality.
2. Use the properties of identity and equality.
Examples
Name the property used in n • 12 = 0. Then f nd the
MO. 7 - L1a value of n.
Recognize The Properties Of n = 0, since 0 • 12 = 0.
Identity And Equality Answer This is the Multiplicative
Property of Zero.
Vocabulary A-Z
1
Let us learn some vocabulary Name the property used in n • = 1. Then f nd the
value of n. 5
1
since n = 5, 5 • = 1. This is the
additive identity Answer 5
Multiplicative Inverse Property.
the sum of any number and 0 is equal to the
number. Thus, 0 is called the additive identity.
5 + 0 = 5 1 + 2 + 0 = 3
Your Turn!
multiplicative identity
Identify Properties
the product of any number and 1 is equal to the
number, 1 is called the multiplicative identity. 1
Name the property used in n • = 1. Then f nd
3
the value of n.
7 x 1 = 7 10 x 1 = 10
A. Multiplicative Inverse Property; n = 3
B. Multiplicative Property of zero; n = 0
multiplicative inverses
C. Multiplicative Inverse Property; n = 1
two numbers whose product is 1 are called 1 3
multiplicative inverses. D. Additive Inverse Property; n =
3
1 x 2 = 1 1 x 5 = 1 Answer
2 5 Name the property used in n + 0 = 11. Then f nd
the value of n.
reciprocal A. Additive Identity Property; n = 0
two numbers whose product is 1 are called reciprocal. B. Multiplicative Identity Property; n = 11
C. Additive Identity Property; n = 11
D. Multiplicative Identity Property; n = 0
1 Zero has no reciprocal because
2 x 2 = 1 any number times 0 is 0. Answer
2