Page 130 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 130
Congruent Triangles
Real World Example
Corresponding Angles
∠D ≅ ∠H, ∠E ≅ ∠G, ∠F ≅ ∠I
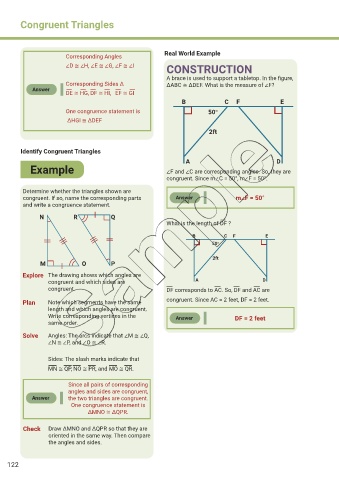
CONSTRUCTION
A brace is used to support a tabletop. In the figure,
Corresponding Sides Δ ΔABC ≅ ΔDEF. What is the measure of ∠F?
Answer
DE ≅ HG, DF ≅ HI, EF ≅ GI
B C F E
One congruence statement is 50°
ΔHGI ≅ ΔDEF
2ft
Identify Congruent Triangles
A D
Example ∠F and ∠C are corresponding angles. So, they are
congruent. Since m∠C = 50°, m∠F = 50°.
Determine whether the triangles shown are
congruent. If so, name the corresponding parts Answer m∠F = 50°
and write a congruence statement.
N R Q
What is the length of DF ?
B C F E
50°
2ft
M O P
Explore The drawing shows which angles are
congruent and which sides are A D
congruent. DF corresponds to AC. So, DF and AC are
Plan Note which segments have the same congruent. Since AC = 2 feet, DF = 2 feet.
length and which angles are congruent.
Write corresponding vertices in the Answer DF = 2 feet
same order.
Solve Angles: The arcs indicate that ∠M ≅ ∠Q,
∠N ≅ ∠P, and ∠O ≅ ∠R.
Sides: The slash marks indicate that
MN ≅ QP, NO ≅ PR, and MO ≅ QR.
Since all pairs of corresponding
angles and sides are congruent,
Answer the two triangles are congruent.
One congruence statement is
ΔMNO ≅ ΔQPR.
Check Draw ΔMNO and ΔQPR so that they are
oriented in the same way. Then compare
the angles and sides.
122