Page 96 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 96
Transformations: Dilations
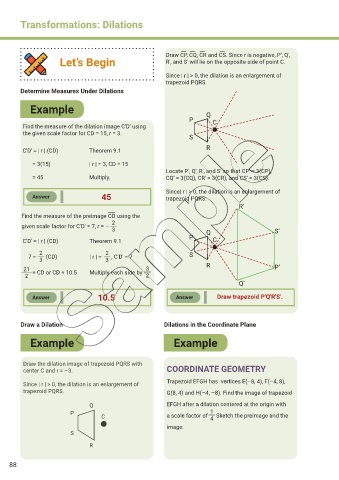
Draw CP, CQ, CR and CS. Since r is negative, P', Q',
Let’s Begin R', and S' will lie on the opposite side of point C.
Since | r | > 0, the dilation is an enlargement of
trapezoid PQRS.
Determine Measures Under Dilations
Example
P Q C
Find the measure of the dilation image C′D′ using
the given scale factor for CD = 15, r = 3.
S
C'D' = | r | (CD) Theorem 9.1 R
= 3(15) | r | = 3, CD = 15
Locate P', Q', R', and S' so that CP' = 3(CP),
= 45 Multiply. CQ' = 3(CQ), CR' = 3(CR), and CS' = 3(CS).
Since| r | > 0, the dilation is an enlargement of
Answer 45 trapezoid PQRS.
R'
Find the measure of the preimage CD using the
2
given scale factor for C'D' = 7, r = –
3 Q S'
P
C'D' = | r | (CD) Theorem 9.1 C
2 2 S
7 = (CD) | r | = , C'D' = 7
3
3
21 3 R P'
= CD or CD = 10.5 Multiply each side by
2 2
Q'
Answer 10.5 Answer Draw trapezoid P'Q'R'S'.
Draw a Dilation Dilations in the Coordinate Plane
Example Example
Draw the dilation image of trapezoid PQRS with
center C and r = –3. COORDINATE GEOMETRY
Since | r | > 0, the dilation is an enlargement of Trapezoid EFGH has vertices E(–8, 4), F(–4, 8),
trapezoid PQRS. G(8, 4) and H(–4, –8). Find the image of trapezoid
Q EFGH after a dilation centered at the origin with
P 1
C a scale factor of Sketch the preimage and the
4
image.
S
R
88