Page 92 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 92
Transformations: Regular Tessellations
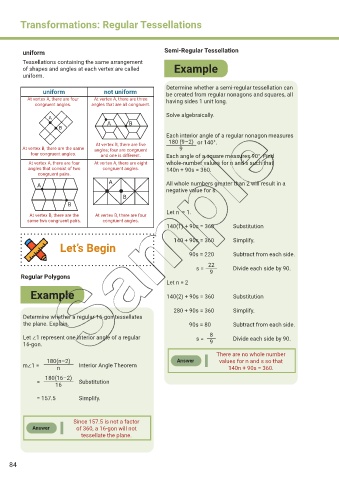
uniform Semi-Regular Tessellation
Tessellations containing the same arrangement
of shapes and angles at each vertex are called Example
uniform.
Determine whether a semi-regular tessellation can
uniform not uniform be created from regular nonagons and squares, all
At vertex A, there are four At vertex A, there are three having sides 1 unit long.
congruent angles. angles that are all congruent.
A Solve algebraically.
A B
B
Each interior angle of a regular nonagon measures
180 (9–2)
At vertex B, there are five or 140°.
At vertex B, there are the same angles; four are congruent 9
four congruent angles. and one is different. Each angle of a square measures 90°. Find
At vertex A, there are four At vertex A, there are eight whole-number values for n and s such that
angles that consist of two congruent angles. 140n + 90s = 360.
congruent pairs.
A All whole numbers greater than 2 will result in a
A
negative value for s.
B
B
Let n = 1.
At vertex B, there are the At vertex B, there are four
same two congruent pairs. congruent angles.
140(1) + 90s = 360 Substitution
140 + 90s = 360 Simplify.
Let’s Begin
90s = 220 Subtract from each side.
22
s = 9 Divide each side by 90.
Regular Polygons
Let n = 2
Example 140(2) + 90s = 360 Substitution
280 + 90s = 360 Simplify.
Determine whether a regular 16-gon tessellates
the plane. Explain. 90s = 80 Subtract from each side.
Let ∠1 represent one interior angle of a regular s = 8 Divide each side by 90.
16-gon. 9
There are no whole number
180(n–2) Answer values for n and s so that
m∠1 = n Interior Angle Theorem 140n + 90s = 360.
180(16–2)
= 16 Substitution
= 157.5 Simplify.
Since 157.5 is not a factor
Answer of 360, a 16-gon will not
tessellate the plane.
84