Page 85 - Math Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 85
Linear Equations
Mo. 3
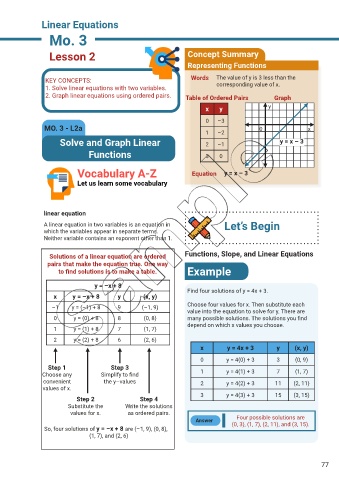
Lesson 2 Concept Summary
Representing Functions
KEY CONCEPTS: Words The value of y is 3 less than the
1. Solve linear equations with two variables. corresponding value of x.
2. Graph linear equations using ordered pairs. Table of Ordered Pairs Graph
x y y
0 –3
MO. 3 - L2a 0 x
1 –2
Solve and Graph Linear 2 –1 y = x – 3
Functions 3 0
Vocabulary A-Z Equation y = x – 3
Let us learn some vocabulary
linear equation
A linear equation in two variables is an equation in Let’s Begin
which the variables appear in separate terms.
Neither variable contains an exponent other than 1.
Solutions of a linear equation are ordered Functions, Slope, and Linear Equations
pairs that make the equation true. One way
to find solutions is to make a table. Example
y = –x + 8
Find four solutions of y = 4x + 3.
x y = –x + 8 y (x, y)
–1 y = (–1) + 8 9 (–1, 9) Choose four values for x. Then substitute each
value into the equation to solve for y. There are
0 y = (0) + 8 8 (0, 8) many possible solutions. The solutions you find
depend on which x values you choose.
1 y = (1) + 8 7 (1, 7)
2 y = (2) + 8 6 (2, 6)
x y = 4x + 3 y (x, y)
0 y = 4(0) + 3 3 (0, 9)
Step 1 Step 3
Choose any Simplify to find 1 y = 4(1) + 3 7 (1, 7)
convenient the y–values 2 y = 4(2) + 3 11 (2, 11)
values of x.
3 y = 4(3) + 3 15 (3, 15)
Step 2 Step 4
Substitute the Write the solutions
values for x. as ordered pairs.
Four possible solutions are
Answer (0, 3), (1, 7), (2, 11), and (3, 15).
So, four solutions of y = –x + 8 are (–1, 9), (0, 8),
(1, 7), and (2, 6)
77