Page 100 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 100
Coordinate Proofs
Mo. 9
Lesson 7
Let’s Begin
KEY CONCEPTS:
Position and Label a Triangle
1. Position and label triangles for use in
coordinate proofs.
2. Write coordinate proofs. Example
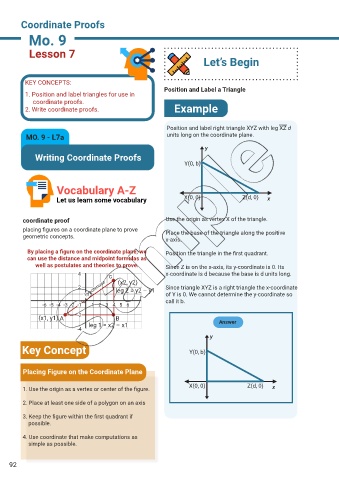
Position and label right triangle XYZ with leg XZ d
MO. 9 - L7a units long on the coordinate plane.
y
Writing Coordinate Proofs
Y(0, b)
Vocabulary A-Z
Let us learn some vocabulary X(0, 0) Z(d, 0) x
coordinate proof Use the origin as vertex X of the triangle.
placing figures on a coordinate plane to prove Place the base of the triangle along the positive
geometric concepts.
x-axis.
By placing a figure on the coordinate plane, we Position the triangle in the first quadrant.
can use the distance and midpoint formulas as
well as postulates and theories to prove. Since Z is on the x-axis, its y-coordinate is 0. Its
4 c x-coordinate is d because the base is d units long.
hypotenuse leg 2 = y2 – y1 of Y is 0. We cannot determine the y-coordinate so
2 (x2, y2) Since triangle XYZ is a right triangle the x-coordinate
call it b.
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6
(x1, y1) A -2 B
leg 1 = x2 – x1 Answer
-4
y
Key Concept Y(0, b)
Placing Figure on the Coordinate Plane
X(0, 0) Z(d, 0) x
1. Use the origin as a vertex or center of the figure.
2. Place at least one side of a polygon on an axis
3. Keep the figure within the first quadrant if
possible.
4. Use coordinate that make computations as
simple as possible.
92