Page 97 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 97
Properties of Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
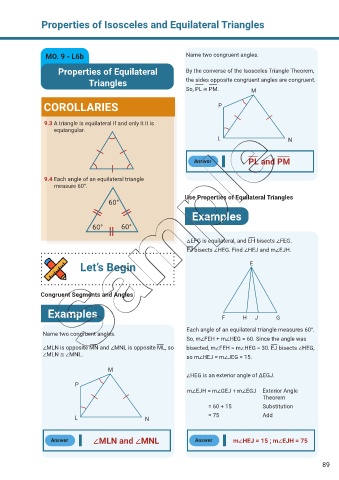
MO. 9 - L6b Name two congruent angles.
Properties of Equilateral By the converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem,
Triangles the sides opposite congruent angles are congruent.
So, PL ≅ PM. M
COROLLARIES P
9.3 A triangle is equilateral if and only it it is
equiangular.
L N
Answer PL and PM
9.4 Each angle of an equilateral triangle
measure 60°.
Use Properties of Equilateral Triangles
60°
Examples
60° 60°
△EFG is equilateral, and EH bisects ∠FEG.
EJ bisects ∠HEG. Find ∠HEJ and m∠EJH.
Let’s Begin E
Congruent Segments and Angles
Examples F H J G
Each angle of an equilateral triangle measures 60°.
Name two congruent angles.
So, m∠FEH + m∠HEG = 60. Since the angle was
∠MLN is opposite MN and ∠MNL is opposite ML, so bisected, m∠FEH = m∠HEG = 30. EJ bisects ∠HEG,
∠MLN ≅ ∠MNL. so m∠HEJ = m∠JEG = 15.
M
∠HEG is an exterior angle of ΔEGJ.
P
m∠EJH = m∠GEJ + m∠EGJ Exterior Angle
Theorem
= 60 + 15 Substitution
L N = 75 Add
Answer ∠MLN and ∠MNL Answer m∠HEJ = 15 ; m∠EJH = 75
89