Page 39 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 39
Quadrilaterals: Coordinate Proofs
Mo. 7
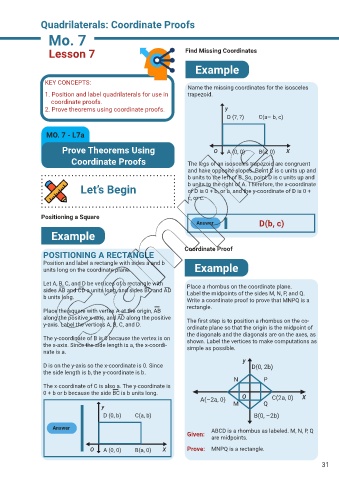
Lesson 7 Find Missing Coordinates
Example
KEY CONCEPTS:
Name the missing coordinates for the isosceles
1. Position and label quadrilaterals for use in trapezoid.
coordinate proofs.
2. Prove theorems using coordinate proofs. y
D (?, ?) C(a– b, c)
MO. 7 - L7a
Prove Theorems Using O A (0, 0) B(a, 0) X
Coordinate Proofs The legs of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent
and have opposite slopes. Point C is c units up and
b units to the left of B. So, point D is c units up and
Let’s Begin b units to the right of A. Therefore, the x-coordinate
of D is 0 + b, or b, and the y-coordinate of D is 0 +
c, or c.
Positioning a Square
Answer D(b, c)
Example
POSITIONING A RECTANGLE Coordinate Proof
Position and label a rectangle with sides a and b
units long on the coordinate plane. Example
Let A, B, C, and D be vertices of a rectangle with Place a rhombus on the coordinate plane.
sides AB and CD a units long, and sides BC and AD Label the midpoints of the sides M, N, P, and Q.
b units long.
Write a coordinate proof to prove that MNPQ is a
rectangle.
Place the square with vertex A at the origin, AB
along the positive x-axis, and AD along the positive The first step is to position a rhombus on the co-
y-axis. Label the vertices A, B, C, and D.
ordinate plane so that the origin is the midpoint of
the diagonals and the diagonals are on the axes, as
The y-coordinate of B is 0 because the vertex is on shown. Label the vertices to make computations as
the x-axis. Since the side length is a, the x-coordi- simple as possible.
nate is a.
y
D is on the y-axis so the x-coordinate is 0. Since D(0, 2b)
the side length is b, the y-coordinate is b.
N P
The x-coordinate of C is also a. The y-coordinate is
0 + b or b because the side BC is b units long.
A(–2a, 0) O C(2a, 0) X
y M Q
D (0, b) C(a, b) B(0, –2b)
Answer ABCD is a rhombus as labeled. M, N, P, Q
Given:
are midpoints.
O A (0, 0) B(a, 0) X Prove: MNPQ is a rectangle.
31