Page 154 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 154
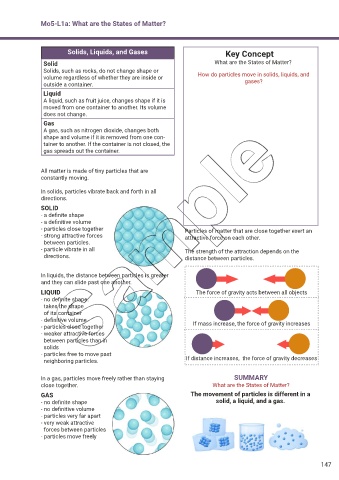
Mo5-L1a: What are the States of Matter?
Solids, Liquids, and Gases Key Concept
Solid What are the States of Matter?
Solids, such as rocks, do not change shape or How do particles move in solids, liquids, and
volume regardless of whether they are inside or
outside a container. gases?
Liquid
A liquid, such as fruit juice, changes shape if it is
moved from one container to another. Its volume
does not change.
Gas
A gas, such as nitrogen dioxide, changes both
shape and volume if it is removed from one con-
tainer to another. If the container is not closed, the
gas spreads out the container.
All matter is made of tiny particles that are
constantly moving.
In solids, particles vibrate back and forth in all
directions.
SOLID
- a definite shape
- a definitive volume
- particles close together Particles of matter that are close together exert an
- strong attractive forces attractive force on each other.
between particles.
- particle vibrate in all The strength of the attraction depends on the
directions. distance between particles.
In liquids, the distance between particles is greater
and they can slide past one another.
LIQUID The force of gravity acts between all objects
- no definite shape:
takes the shape
of its container
- definitive volume
- particles close together If mass increase, the force of gravity increases
- weaker attractive forces
between particles than in
solids
- particles free to move past
neighboring particles. If distance increases, the force of gravity decreases
In a gas, particles move freely rather than staying SUMMARY
close together. What are the States of Matter?
GAS The movement of particles is different in a
- no definite shape solid, a liquid, and a gas.
- no definitive volume
- particles very far apart
- very weak attractive
forces between particles
- particles move freely
147