Page 72 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 72
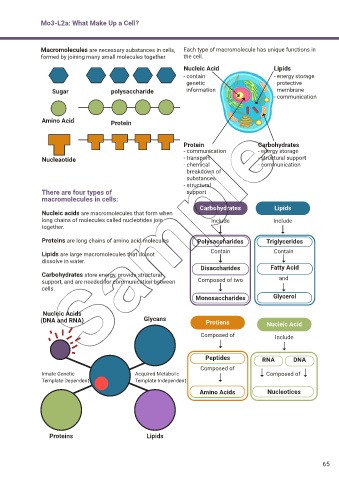
Mo3-L2a: What Make Up a Cell?
Macromolecules are necessary substances in cells, Each type of macromolecule has unique functions in
formed by joining many small molecules together the cell.
Nucleic Acid Lipids
- contain - energy storage
genetic protective
Sugar polysaccharide information membrane
- communication
Amino Acid Protein
Protein Carbohydrates
- communication - energy storage
Nucleaotide - transport - structural support
- chemical - communication
breakdown of
substances
- structural
There are four types of support
macromolecules in cells:
Carbohydrates Lipids
Nucleic acids are macromolecules that form when
long chains of molecules called nucleotides join Include Include
together.
Proteins are long chains of amino acid molecules Polysaccharides Triglycerides
Lipids are large macromolecules that do not Contain Contain
dissolve in water.
Disaccharides Fatty Acid
Carbohydrates store energy, provide structural and
support, and are needed for communication between Composed of two
cells.
Monosaccharides Glycerol
Nucleic Acids
(DNA and RNA) Glycans Protiens Nucleic Acid
Composed of Include
Peptides RNA DNA
Composed of
Innate Genetic Acquired Metabolic Composed of
Template-Dependent Template-Independent
Amino Acids Nucleotices
Proteins Lipids
65