Page 80 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 80
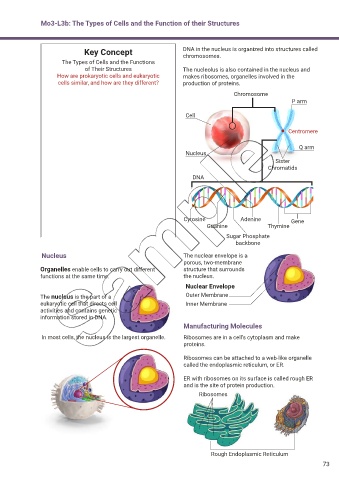
Mo3-L3b: The Types of Cells and the Function of their Structures
Key Concept DNA in the nucleus is organized into structures called
chromosomes.
The Types of Cells and the Functions
of Their Structures The nucleolus is also contained in the nucleus and
How are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic makes ribosomes, organelles involved in the
cells similar, and how are they different? production of proteins.
Chromosome
P arm
Cell
Centromere
Q arm
Nucleus
Sister
Chromatids
DNA
Cytosine Adenine Gene
Guanine Thymine
Sugar Phosphate
backbone
Nucleus The nuclear envelope is a
porous, two-membrane
Organelles enable cells to carry out different structure that surrounds
functions at the same time. the nucleus.
Nuclear Envelope
The nucleus is the part of a Outer Membrane
eukaryotic cell that directs cell Inner Membrane
activities and contains genetic
information stored in DNA.
Manufacturing Molecules
In most cells, the nucleus is the largest organelle. Ribosomes are in a cell’s cytoplasm and make
proteins.
Ribosomes can be attached to a web-like organelle
called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER.
ER with ribosomes on its surface is called rough ER
and is the site of protein production.
Ribosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
73