Page 22 - Science Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 22
Mo7-L2a: What are Physical Properties of Matter?
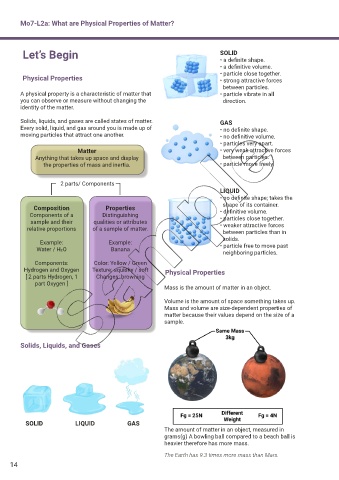
Let’s Begin SOLID
• a def nite shape.
• a def nitive volume.
• particle close together.
Physical Properties • strong attractive forces
between particles.
A physical property is a characteristic of matter that • particle vibrate in all
you can observe or measure without changing the direction.
identity of the matter.
Solids, liquids, and gases are called states of matter. GAS
Every solid, liquid, and gas around you is made up of • no def nite shape.
moving particles that attract one another. • no def nitive volume.
• particles very apart.
Matter • very weak attractive forces
Anything that takes up space and display between particles.
the properties of mass and inertia. • particle move freely.
2 parts/ Components
LIQUID
• no def nite shape; takes the
shape of its container.
Composition Properties • def nitive volume.
Components of a Distinguishing • particles close together.
sample and their qualities or attributes • weaker attractive forces
relative proportions of a sample of matter.
between particles than in
solids.
Example: Example: • particle free to move past
Water / H2O Banana
neighboring particles.
Components: Color: Yellow / Green
Hydrogen and Oxygen Texture: squishy / soft Physical Properties
[ 2 parts Hydrogen, 1 Changes: browning
part Oxygen ]
Mass is the amount of matter in an object.
Volume is the amount of space something takes up.
Mass and volume are size-dependent properties of
matter because their values depend on the size of a
sample.
Solids, Liquids, and Gases
SOLID LIQUID GAS
The amount of matter in an object, measured in
grams(g) A bowling ball compared to a beach ball is
heavier therefore has more mass.
The Earth has 9.3 times more mass than Mars.
14