Page 267 - Science Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 267
Mo7-L4b: What are Chemical Equations?
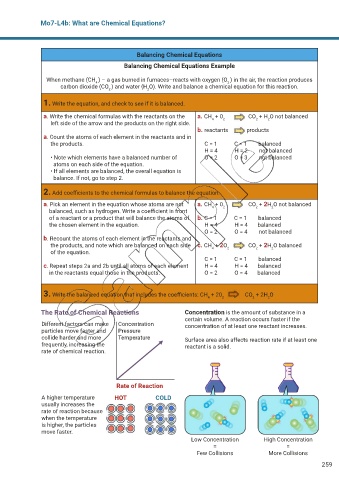
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing Chemical Equations Example
When methane (CH ) – a gas burned in furnaces–reacts with oxygen (O ) in the air, the reaction produces
4
2
carbon dioxide (CO ) and water (H O). Write and balance a chemical equation for this reaction.
2 2
1. Write the equation, and check to see if it is balanced.
a. Write the chemical formulas with the reactants on the a. CH + 0 CO + H O not balanced
4
2
2
2
left side of the arrow and the products on the right side.
b. reactants products
a. Count the atoms of each element in the reactants and in
the products. C = 1 C = 1 balanced
H = 4 H = 2 not balanced
• Note which elements have a balanced number of O = 2 O = 3 not balanced
atoms on each side of the equation.
• If all elements are balanced, the overall equation is
balance. If not, go to step 2.
2. Add coefficients to the chemical formulas to balance the equation.
a. Pick an element in the equation whose atoms are not a. CH + 0 CO + 2H O not balanced
2
4
2
2
balanced, such as hydrogen. Write a coefficient in front
of a reactant or a product that will balance the atoms of b. C = 1 C = 1 balanced
the chosen element in the equation. H = 4 H = 4 balanced
O = 2 O = 4 not balanced
b. Recount the atoms of each element in the reactants and
the products, and note which are balanced on each side c. CH + 2O CO + 2H O balanced
2
2
2
4
of the equation.
C = 1 C = 1 balanced
c. Repeat steps 2a and 2b until all atoms of each element H = 4 H = 4 balanced
in the reactants equal those in the products. O = 2 O = 4 balanced
3. Write the balanced equation that includes the coefficients: CH + 20 CO + 2H O
2
2
2
4
The Rate of Chemical Reactions Concentration is the amount of substance in a
certain volume. A reaction occurs faster if the
Different factors can make Concentration concentration of at least one reactant increases.
particles move faster and Pressure
collide harder and more Temperature Surface area also affects reaction rate if at least one
frequently, increasing the reactant is a solid.
rate of chemical reaction.
Rate of Reaction
A higher temperature HOT COLD
usually increases the
rate of reaction because
when the temperature
is higher, the particles
move faster.
Low Concentration High Concentration
= =
Few Collisions More Collisions
259