Page 93 - Math Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 93
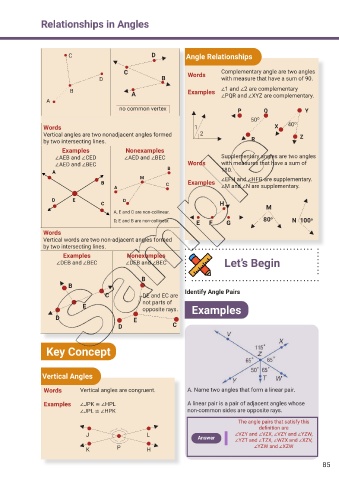
Relationships in Angles
C D Angle Relationships
C Words Complementary angle are two angles
D B with measure that have a sum of 90.
B Examples ∠1 and ∠2 are complementary
A ∠PQR and ∠XYZ are complementary.
A
no common vertex P Q Y
50 O
Words 1 X 40 O
Vertical angles are two nonadjacent angles formed 2 Z
by two intersecting lines. R
Examples Nonexamples
∠AEB and ∠CED ∠AED and ∠BEC Supplementary angles are two angles
∠AED and ∠BEC Words with measures that have a sum of
B 180.
M ∠EFH and ∠HFG are supplementary.
C Examples ∠M and ∠N are supplementary.
A
D
H M
A, E and C are non-collinear.
D, E and B are non-collinear. E F G 80 o N 100 o
Words
Vertical words are two non-adjacent angles formed
by two intersecting lines.
Examples Nonexamples
∠DEB and ∠BEC ∠DEB and ∠BEC Let’s Begin
B
B
C DE and EC are Identify Angle Pairs
not parts of
E opposite rays. Examples
D E
D C
Key Concept
Vertical Angles
Words Vertical angles are congruent. A. Name two angles that form a linear pair.
Examples ∠JPK ≌ ∠HPL A linear pair is a pair of adjacent angles whose
∠JPL ≌ ∠HPK non-common sides are opposite rays.
The angle pairs that satisfy this
def nition are
J L ∠VZY and ∠VZX, ∠VZY and ∠YZW,
Answer ∠YZT and ∠TZX, ∠WZX and ∠XZV,
K P H ∠YZW and ∠XZW
85