Page 104 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 104
Transformations: Using Vectors
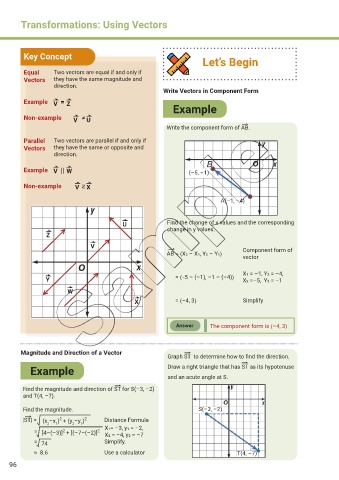
Key Concept
Let’s Begin
Equal Two vectors are equal if and only if
Vectors they have the same magnitude and
direction.
Write Vectors in Component Form
Example = Z
V
Example
Non-example V U
≠
Write the component form of AB.
Parallel Two vectors are parallel if and only if
Vectors they have the same or opposite and
direction.
V
Example || W (–5, –1)
Non-example ∦ X
V
A(–1, –4)
U Find the change of x values and the corresponding
change in y values.
Z
V
Component form of
AB = 〈X2 – X1, Y2 – Y1〉
vector
X1 = –1, Y2 = –4,
Y = 〈–5 – (–1), –1 – (–4)〉 X2 =–5, Y2 = –1
W
X = 〈–4, 3〉 Simplify
Answer The component form is 〈–4, 3〉
Magnitude and Direction of a Vector
Graph ST to determine how to find the direction.
Example Draw a right triangle that has ST as its hypotenuse
and an acute angle at S.
Find the magnitude and direction of ST for S(–3, –2)
and T(4, –7).
Find the magnitude. S(–3, –2)
2
|ST| = (x –x ) + (y –y ) 2 Distance Formula
2 1 2 1
= [4–(–3)] + [(–7–(–2)] 2 X1= –3, y1 = –2,
2
X2 = –4, y2 = –7
= 74 Simplify.
≈ 8.6 Use a calculator T(4, –7)
96