Page 82 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 82
Transformations: Translated Images
Find a Translation Using Reflections
To find the translation from raindrop 2 to raindrop
3, use the coordinates at the top of each raindrop.
Use the coordinates (1, 2) and (–1, –1) in the Example
formula.
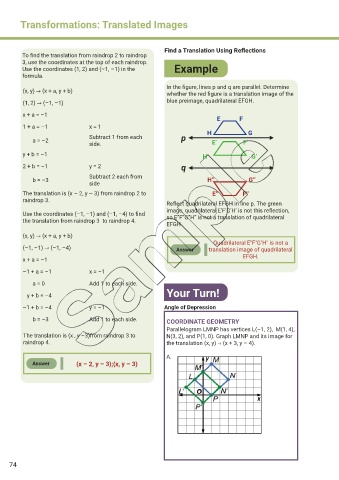
In the figure, lines p and q are parallel. Determine
(x, y) → (x + a, y + b) whether the red figure is a translation image of the
(1, 2) → (–1, –1) blue preimage, quadrilateral EFGH.
x + a = –1
E F
1 + a = –1 x = 1
Subtract 1 from each p H G
a = –2 E’ F’
side.
y + b = –1 H’ G’
2 + b = –1 y = 2 q
Subtract 2 each from
b = –3 H’’ G’’
side
The translation is (x – 2, y – 3) from raindrop 2 to E’’ F’’
raindrop 3.
Reflect quadrilateral EFGH in line p. The green
image, quadrilateral E’F’G’H’ is not this reflection,
Use the coordinates (–1, –1) and (–1, –4) to find so E’’F’’G’’H’‘ is not a translation of quadrilateral
the translation from raindrop 3 to raindrop 4.
EFGH
(x, y) → (x + a, y + b)
Quadrilateral E''F''G''H'' is not a
(–1, –1) → (–1, –4) Answer translation image of quadrilateral
EFGH.
x + a = –1
–1 + a = –1 x = –1
a = 0 Add 1 to each side.
y + b = –4 Your Turn!
–1 + b = –4 y = –1 Angle of Depression
b = –3 Add 1 to each side. COORDINATE GEOMETRY
Parallelogram LMNP has vertices L(–1, 2), M(1, 4),
The translation is (x , y –3)from raindrop 3 to N(3, 2), and P(1, 0). Graph LMNP and its image for
raindrop 4. the translation (x, y) (x + 3, y – 4).
A.
Answer (x – 2, y – 3);(x, y – 3)
74