Page 87 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 87
Transformations: Rotated Images
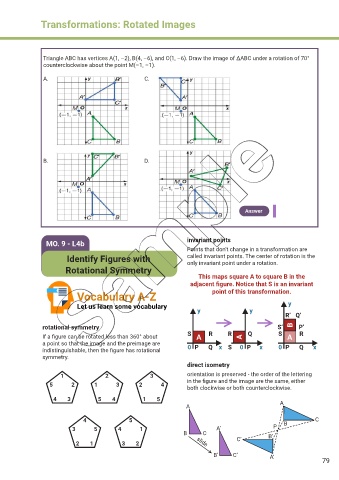
Triangle ABC has vertices A(1, –2), B(4, –6), and C(1, –6). Draw the image of ΔABC under a rotation of 70°
counterclockwise about the point M(–1, –1).
A. C.
B. D.
Answer
MO. 9 - L4b invariant points
Points that don’t change in a transformation are
Identify Figures with called invariant points. The center of rotation is the
only invariant point under a rotation.
Rotational Symmetry
This maps square A to square B in the
adjacent figure. Notice that S is an invariant
Vocabulary A-Z point of this transformation.
Let us learn some vocabulary y
y y
R’ Q’
rotational symmetry S’ B P’
If a figure can be rotated less than 360° about S A R R A Q S A R
a point so that the image and the preimage are 0 P Q x S 0 P x 0 P Q x
indistinguishable, then the figure has rotational
symmetry.
direct isometry
1 2 3 orientation is preserved - the order of the lettering
5 2 1 3 2 4 in the figure and the image are the same, either
both clockwise or both counterclockwise.
4 3 5 4 1 5
A A
4 5 B C
3 5 4 1 A’ P
B C B’
C’
2 1 3 2 slide
B’ C’ A’
79