Page 47 - Math Course 3 (Book 1)
P. 47
Quadratic Equations
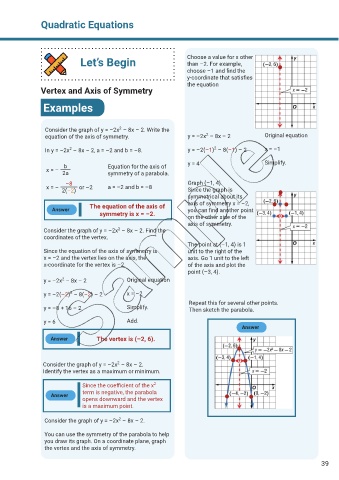
Let’s Begin Choose a value for x other
than –2. For example,
choose –1 and find the
y-coordinate that satisfies
the equation
Vertex and Axis of Symmetry
Examples
Consider the graph of y = –2x – 8x – 2. Write the
2
2
equation of the axis of symmetry. y = –2x – 8x – 2 Original equation
2
2
In y = –2x – 8x – 2, a = –2 and b = –8. y = –2(–1) – 8(–1) – 2 x = –1
b Equation for the axis of y = 4 Simplify.
x = –
2a symmetry of a parabola.
–8 Graph (–1, 4).
x = – 2(–2) or –2 a = –2 and b = –8 Since the graph is
symmetrical about its
The equation of the axis of axis of symmetry x = –2,
Answer you can find another point
symmetry is x = –2. on the other side of the
axis of symmetry.
2
Consider the graph of y = –2x – 8x – 2. Find the
coordinates of the vertex.
The point at (–1, 4) is 1
Since the equation of the axis of symmetry is unit to the right of the
x = –2 and the vertex lies on the axis, the axis. Go 1 unit to the left
x-coordinate for the vertex is –2. of the axis and plot the
point (–3, 4).
2
y = –2x – 8x – 2 Original equation
2
y = –2(–2) – 8(–2) – 2 x = –2
Repeat this for several other points.
y = –8 + 16 – 2 Simplify. Then sketch the parabola.
y = 6 Add.
Answer
Answer The vertex is (–2, 6).
2
Consider the graph of y = –2x – 8x – 2.
Identify the vertex as a maximum or minimum.
2
Since the coefficient of the x
term is negative, the parabola
Answer
opens downward and the vertex
is a maximum point.
Consider the graph of y = –2x – 8x – 2.
2
You can use the symmetry of the parabola to help
you draw its graph. On a coordinate plane, graph
the vertex and the axis of symmetry.
39