Page 49 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 49
Geometric Surface Area: Pyramids
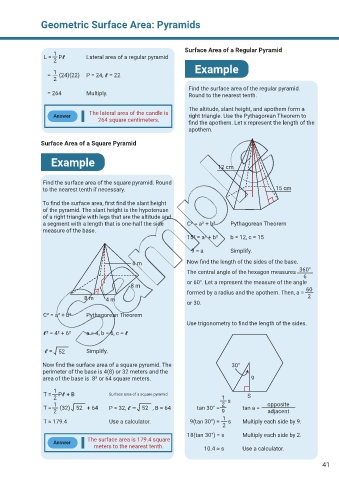
Surface Area of a Regular Pyramid
1
L = P Lateral area of a regular pyramid
2 Example
1
= (24)(22) P = 24, = 22
2
Find the surface area of the regular pyramid.
= 264 Multiply. Round to the nearest tenth.
The altitude, slant height, and apothem form a
The lateral area of the candle is
Answer right triangle. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to
264 square centimeters. find the apothem. Let x represent the length of the
apothem.
Surface Area of a Square Pyramid
Example 12 cm
Find the surface area of the square pyramid. Round
to the nearest tenth if necessary. 15 cm
To find the surface area, first find the slant height
of the pyramid. The slant height is the hypotenuse
of a right triangle with legs that are the altitude and
a segment with a length that is one-half the side C² = a² + b² Pythagorean Theorem
measure of the base.
15² = a² + b² b = 12, c = 15
9 = a Simplify.
6 m Now find the length of the sides of the base.
360°
The central angle of the hexagon measures
6
or 60°. Let a represent the measure of the angle
8 m
formed by a radius and the apothem. Then, a = 60
8 m 4 m or 30. 2
C² = a² + b² Pythagorean Theorem
Use trigonometry to find the length of the sides.
² = 4² + 6² a = 4, b = 6, c =
= 52 Simplify.
Now find the surface area of a square pyramid. The 30°
perimeter of the base is 4(8) or 32 meters and the
area of the base is 8² or 64 square meters. 9
1
T = P + B Surface area of a square pyramid S
2 1 s
1 2 opposite
52
T = (32) + 64 P = 32, = , B = 64 tan 30° = tan a =
52
2 9 adjacent
1
T ≈ 179.4 Use a calculator. 9(tan 30°) = s Multiply each side by 9.
2
18(tan 30°) = s Multiply each side by 2.
The surface area is 179.4 square
Answer
meters to the nearest tenth. 10.4 ≈ s Use a calculator.
41