Page 77 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 77
Angle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems
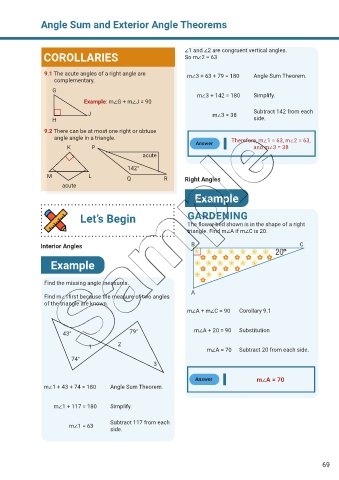
∠1 and ∠2 are congruent vertical angles.
COROLLARIES So m∠2 = 63
9.1 The acute angles of a right angle are m∠3 + 63 + 79 = 180 Angle Sum Theorem.
complementary.
G
m∠3 + 142 = 180 Simplify.
Example: m∠G + m∠J = 90
J m∠3 = 38 Subtract 142 from each
H side.
9.2 There can be at most one right or obtuse
angle angle in a triangle.
Answer Therefore, m∠1 = 63, m∠2 = 63,
K P and m∠3 = 38
acute
142°
M L Q R Right Angles
acute
Example
Let’s Begin GARDENING
The flower bed shown is in the shape of a right
triangle. Find m∠A if m∠C is 20.
Interior Angles B C
Example
Find the missing angle measures.
A
Find m∠1first because the measure of two angles
of the triangle are known.
m∠A + m∠C = 90 Corollary 9.1
43° 79° m∠A + 20 = 90 Substitution
1 2
m∠A = 70 Subtract 20 from each side.
74°
3
Answer m∠A = 70
m∠1 + 43 + 74 = 180 Angle Sum Theorem.
m∠1 + 117 = 180 Simplify.
Subtract 117 from each
m∠1 = 63
side.
69