Page 73 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 73
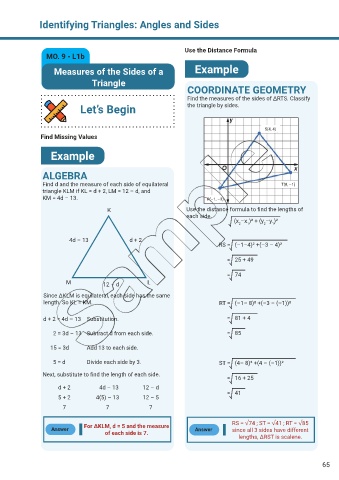
Identifying Triangles: Angles and Sides
Use the Distance Formula
MO. 9 - L1b
Measures of the Sides of a Example
Triangle
COORDINATE GEOMETRY
Find the measures of the sides of ΔRTS. Classify
Let’s Begin the triangle by sides.
S(4, 4)
Find Missing Values
Example
ALGEBRA
Find d and the measure of each side of equilateral T(8, –1)
triangle KLM if KL = d + 2, LM = 12 – d, and
KM = 4d – 13. R(–1, –3)
K Use the distance formula to find the lengths of
each side.
(x –x )² + (y –y )²
2
1
2
1
4d – 13 d + 2
RS = (–1–4)² +(–3 – 4)²
= 25 + 49
= 74
M 12 – d L
Since ΔKLM is equilateral, each side has the same
length. So KL = KM. RT = (–1– 8)² +(–3 – (–1))²
d + 2 = 4d – 13 Substitution. = 81 + 4
2 = 3d – 13 Subtract d from each side. = 85
15 = 3d Add 13 to each side.
5 = d Divide each side by 3. ST = (4– 8)² +(4 – (–1))²
Next, substitute to find the length of each side.
= 16 + 25
d + 2 4d – 13 12 – d
= 41
5 + 2 4(5) – 13 12 – 5
7 7 7
For ΔKLM, d = 5 and the measure RS = √74 ; ST = √41 ; RT = √85
Answer Answer since all 3 sides have different
of each side is 7.
lengths, ΔRST is scalene.
65