Page 76 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 76
Angle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems
Mo. 9
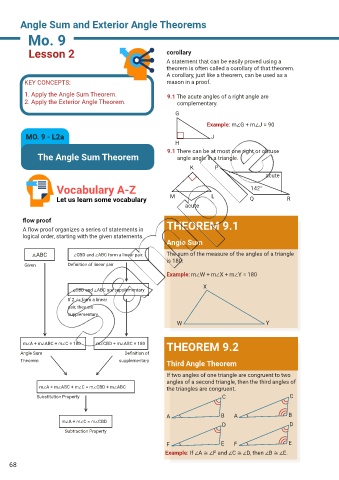
Lesson 2 corollary
A statement that can be easily proved using a
theorem is often called a corollary of that theorem.
A corollary, just like a theorem, can be used as a
KEY CONCEPTS: reason in a proof.
1. Apply the Angle Sum Theorem. 9.1 The acute angles of a right angle are
2. Apply the Exterior Angle Theorem. complementary.
G
Example: m∠G + m∠J = 90
MO. 9 - L2a J
H
9.1 There can be at most one right or obtuse
The Angle Sum Theorem angle angle in a triangle.
K P
acute
Vocabulary A-Z 142°
Let us learn some vocabulary M L Q R
acute
flow proof THEOREM 9.1
A flow proof organizes a series of statements in
logical order, starting with the given statements.
Angle Sum
△ABC ∠CBD and ∠ABC form a linear pair. The sum of the measure of the angles of a triangle
is 180.
Given Definition of linear pair
Example: m∠W + m∠X + m∠Y = 180
X
∠CBD and ∠ABC are supplementary
If 2 ∠s form a linear
pair, they are
supplementary.
W Y
THEOREM 9.2
m∠A + m∠ABC + m∠C = 180 m∠CBD + m∠ABC = 180
Angle Sum Definition of
Theorem supplementary Third Angle Theorem
If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two
angles of a second triangle, then the third angles of
m∠A + m∠ABC + m∠C = m∠CBD + m∠ABC the triangles are congruent.
Substitution Property C C
A B A B
m∠A + m∠C = m∠CBD
D D
Subtraction Property
F E F E
Example: If ∠A ≅ ∠F and ∠C ≅ ∠D, then ∠B ≅ ∠E.
68