Page 83 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 83
Congruent Triangles
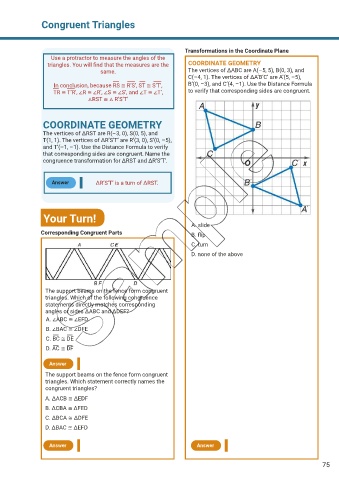
Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
Use a protractor to measure the angles of the
triangles. You will find that the measures are the COORDINATE GEOMETRY
same. The vertices of ΔABC are A(–5, 5), B(0, 3), and
C(–4, 1). The vertices of ΔA’B’C’ are A’(5, –5),
In conclusion, because RS ≅ R’S’, ST ≅ S’T’, B’(0, –3), and C’(4, –1). Use the Distance Formula
TR ≅ T’R’, ∠R ≅ ∠R’, ∠S ≅ ∠S’, and ∠T ≅ ∠T’, to verify that corresponding sides are congruent.
△RST ≅ △ R’S’T’
COORDINATE GEOMETRY
The vertices of ΔRST are R(–3, 0), S(0, 5), and
T(1, 1). The vertices of ΔR’S’T’ are R’(3, 0), S’(0, –5),
and T’(–1, –1). Use the Distance Formula to verify
that corresponding sides are congruent. Name the
congruence transformation for ΔRST and ΔR’S’T’.
Answer ΔR’S’T’ is a turn of ΔRST.
Your Turn!
A. slide
Corresponding Congruent Parts B. flip
C. turn
D. none of the above
The support beams on the fence form congruent
triangles. Which of the following congruence
statements directly matches corresponding
angles or sides ΔABC and ΔDEF?
A. ∠ABC ≅ ∠EFD
B. ∠BAC ≅ ∠DFE
C. BC ≅ DE
D. AC ≅ DF
Answer
The support beams on the fence form congruent
triangles. Which statement correctly names the
congruent triangles?
A. ΔACB ≅ ΔEDF
B. ΔCBA ≅ ΔFED
C. ΔBCA ≅ ΔDFE
D. ΔBAC ≅ ΔEFD
Answer Answer
75