Page 100 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 100
Mo3-L6a: What is Cellular Respiration?
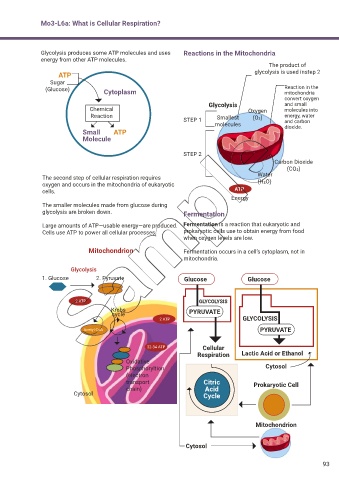
Glycolysis produces some ATP molecules and uses Reactions in the Mitochondria
energy from other ATP molecules.
The product of
ATP glycolysis is used instep 2
Sugar
(Glucose) Cytoplasm Reaction in the
mitochondria
convert oxygen
Glycolysis and small
Chemical Oxygen molecules into
Reaction Smallest (O2) energy, water
STEP 1 and carbon
molecules dioxide.
Small ATP
Molecule
STEP 2
Carbon Dioxide
(CO2)
The second step of cellular respiration requires Water
oxygen and occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic (H2O)
cells. ATP
Energy
The smaller molecules made from glucose during
glycolysis are broken down. Fermentation
Large amounts of ATP—usable energy—are produced. Fermentation is a reaction that eukaryotic and
Cells use ATP to power all cellular processes. prokaryotic cells use to obtain energy from food
when oxygen levels are low.
Mitochondrion Fermentation occurs in a cell’s cytoplasm, not in
mitochondria.
Glycolysis
1. Glucose 2. Pyruvate Glucose Glucose
2 ATP GLYCOLYSIS
Krebs PYRUVATE
cycle
2 ATP GLYCOLYSIS
Acetyl CoA PYRUVATE
32-34 ATP Cellular
Respiration Lactic Acid or Ethanol
Oxidative
Phosphoryltion Cytosol
(electron
transport Citric Prokaryotic Cell
chain) Acid
Cytosol Cycle
Mitochondrion
Cytosol
93