Page 99 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 99
Cells: Obtaining Energy and Food Making Mo3-L6a: What is Cellular Respiration?
Lesson 6
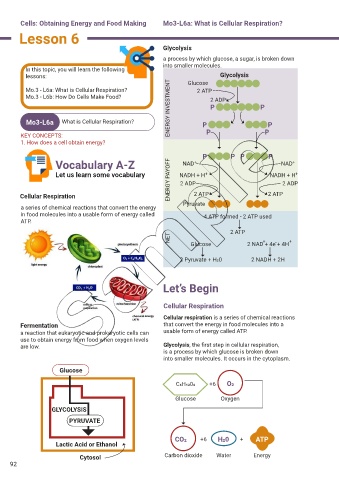
Glycolysis
a process by which glucose, a sugar, is broken down
into smaller molecules.
In this topic, you will learn the following
lessons: Glucose Glycolysis
ENERGY INVESTMENT P P
Mo.3 - L6a: What is Cellular Respiration? 2 ATP
Mo.3 - L6b: How Do Cells Make Food? 2 ADP
Mo3-L6a What is Cellular Respiration? P P
KEY CONCEPTS: P P
1. How does a cell obtain energy?
P P P P
Vocabulary A-Z NAD + NAD +
Let us learn some vocabulary ENERGY PAYOFF NADH + H + NADH + H +
2 ADP
2 ADP
Cellular Respiration 2 ATP 2 ATP
a series of chemical reactions that convert the energy Pyruvate
in food molecules into a usable form of energy called 4 ATP formed - 2 ATP used
ATP. 2 ATP
NET 2 Pyruvate + H20 2 NAD + 4e + 4H +
-
+
Glucose
2 NADH + 2H
Let’s Begin
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions
Fermentation that convert the energy in food molecules into a
a reaction that eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells can usable form of energy called ATP.
use to obtain energy from food when oxygen levels
are low. Glycolysis, the first step in cellular respiration,
is a process by which glucose is broken down
into smaller molecules. It occurs in the cytoplasm.
Glucose
C6H1206 +6 O2
Glucose Oxygen
GLYCOLYSIS
PYRUVATE
CO2 +6 H20 + ATP
Lactic Acid or Ethanol
Cytosol Carbon dioxide Water Energy
92