Page 11 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 11
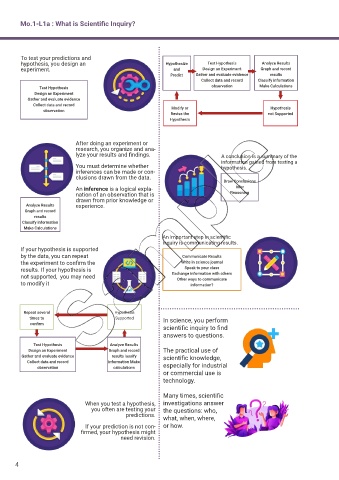
Mo.1-L1a : What is Scientific Inquiry?
To test your predictions and
hypothesis, you design an Hypothesize Test Hypothesis Analyze Results
experiment. and Design an Experiment Graph and record
Predict Gather and evaluate evidence results
Collect data and record Classify information
Test Hypothesis observation Make Calculations
Design an Experiment
Gather and evaluate evidence
Collect data and record Modify or Hypothesis
observation
Revise the not Supported
Hypothesis
After doing an experiment or
research, you organize and ana-
lyze your results and findings. A conclusion is a summary of the
information gained from testing a
You must determine whether hypothesis.
inferences can be made or con-
clusions drawn from the data.
Draw Conclusions
An inference is a logical expla- Infer
nation of an observation that is Reasoning
drawn from prior knowledge or
Analyze Results experience.
Graph and record
results
Classify information
Make Calculations
An important step in scientific
inquiry is communicating results.
If your hypothesis is supported
by the data, you can repeat Communicate Results
the experiment to confirm the Write in science journal
results. If your hypothesis is Speak to your class
not supported, you may need Exchange information with others
Other ways to communicate
to modify it information?
Repeat several Hypothesis
times to Supported In science, you perform
confirm
scientific inquiry to find
answers to questions.
Test Hypothesis Analyze Results
Design an Experiment Graph and record The practical use of
Gather and evaluate evidence results lassify scientific knowledge,
Collect data and record information Make
observation calculations especially for industrial
or commercial use is
technology.
Many times, scientific
When you test a hypothesis, investigations answer
you often are testing your the questions: who,
predictions. what, when, where,
If your prediction is not con- or how.
firmed, your hypothesis might
need revision.
4