Page 94 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 94
Mo3-L5a: How Does Material Enter and Leave Cells?
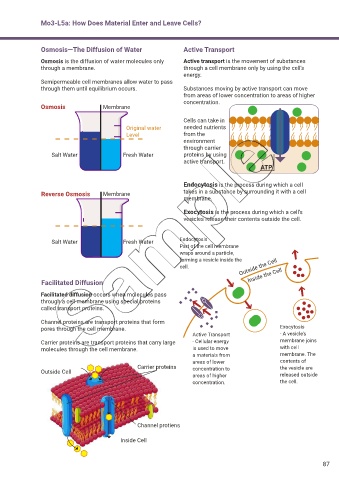
Osmosis—The Diffusion of Water Active Transport
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules only Active transport is the movement of substances
through a membrane. through a cell membrane only by using the cell’s
energy.
Semipermeable cell membranes allow water to pass
through them until equilibrium occurs. Substances moving by active transport can move
from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher
concentration.
Osmosis Membrane
Cells can take in
Original water needed nutrients
Level from the
environment
through carrier
Salt Water Fresh Water proteins by using
active transport.
ATP
Endocytosis is the process during which a cell
Reverse Osmosis Membrane takes in a substance by surrounding it with a cell
membrane.
Exocytosis is the process during which a cell’s
vesicles release their contents outside the cell.
Salt Water Fresh Water Endocytosis
Part of the cell membrane
wraps around a particle,
forming a vesicle inside the
cell. Outside the Cell
Facilitated Diffusion Inside the Cell
Facilitated diffusion occurs when molecules pass
through a cell membrane using special proteins
called transport proteins.
Channel proteins are transport proteins that form
pores through the cell membrane. Exocytosis
Active Transport - A vesicle’s
Carrier proteins are transport proteins that carry large - Cellular energy membrane joins
molecules through the cell membrane. is used to move with cell
a materials from membrane. The
areas of lower contents of
Carrier proteins concentration to the vesicle are
Outside Cell
areas of higher released outside
concentration. the cell.
Channel protiens
Inside Cell
87