Page 91 - Science Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 91
Mo10-L6a: How Do Ref ections and Mirrors Work?
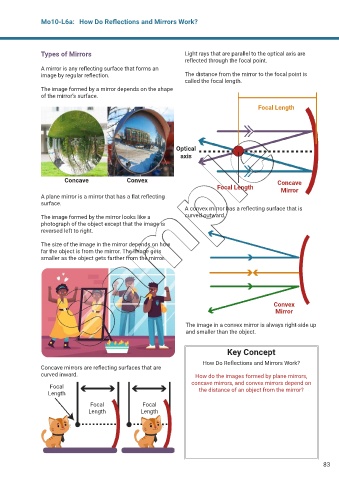
Types of Mirrors Light rays that are parallel to the optical axis are
ref ected through the focal point.
A mirror is any ref ecting surface that forms an
image by regular ref ection. The distance from the mirror to the focal point is
called the focal length.
The image formed by a mirror depends on the shape
of the mirror’s surface.
Focal Length
Optical
axis
Concave Convex Concave
Focal Length Mirror
A plane mirror is a mirror that has a f at ref ecting
surface.
A convex mirror has a ref ecting surface that is
The image formed by the mirror looks like a curved outward.
photograph of the object except that the image is
reversed left to right.
The size of the image in the mirror depends on how
far the object is from the mirror. The image gets
smaller as the object gets farther from the mirror.
Convex
Mirror
The image in a convex mirror is always right-side up
and smaller than the object.
Key Concept
How Do Ref ections and Mirrors Work?
Concave mirrors are ref ecting surfaces that are
curved inward. How do the images formed by plane mirrors,
concave mirrors, and convex mirrors depend on
Focal
Length the distance of an object from the mirror?
Focal Focal
Length Length
83