Page 115 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 115
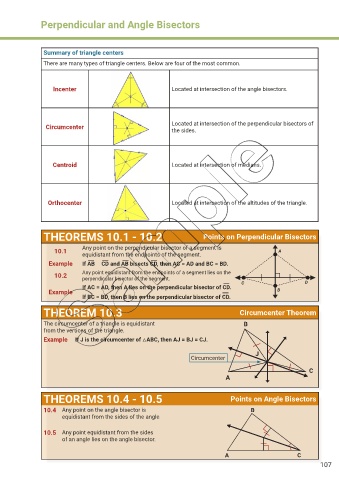
Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors
Summary of triangle centers
There are many types of triangle centers. Below are four of the most common.
Incenter Located at intersection of the angle bisectors.
Circumcenter Located at intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of
the sides.
Centroid Located at intersection of medians.
Orthocenter Located at intersection of the altitudes of the triangle.
THEOREMS 10.1 - 10.2 Points on Perpendicular Bisectors
Any point on the perpendicular bisector of a segment is
10.1 A
equidistant from the endpoints of the segment.
Example If AB ⟂ CD and AB bisects CD, then AC = AD and BC = BD.
10.2 Any point equidistant from the endpoints of a segment lies on the
perpendicular bisector of the segment.
If AC = AD, then A lies on the perpendicular bisector of CD. C D
Example B
If BC = BD, then B lies on the perpendicular bisector of CD.
THEOREM 10.3 Circumcenter Theorem
The circumcenter of a triangle is equidistant B
from the vertices of the triangle.
Example If J is the circumcenter of △ABC, then AJ = BJ = CJ.
J
Circumcenter
C
A
THEOREMS 10.4 - 10.5 Points on Angle Bisectors
10.4 Any point on the angle bisector is B
equidistant from the sides of the angle
10.5 Any point equidistant from the sides
of an angle lies on the angle bisector.
A C
107