Page 116 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 116
Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors
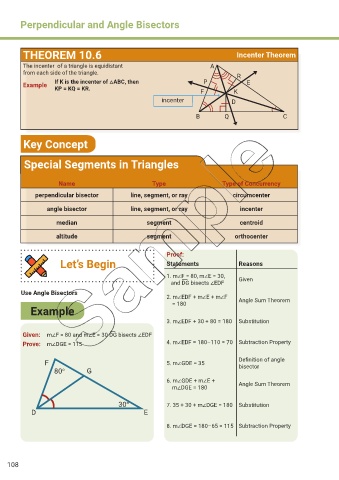
THEOREM 10.6 Incenter Theorem
The incenter of a triangle is equidistant A
from each side of the triangle. R
Example If K is the incenter of △ABC, then P E
KP = KQ = KR. F K
incenter D
B Q C
Key Concept
Special Segments in Triangles
Name Type Type of Concurrency
perpendicular bisector line, segment, or ray circumcenter
angle bisector line, segment, or ray incenter
median segment centroid
altitude segment orthocenter
Proof:
Let’s Begin Statements Reasons
1. m∠F = 80, m∠E = 30, Given
and DG bisects ∠EDF
Use Angle Bisectors
2. m∠EDF + m∠E + m∠F Angle Sum Theorem
= 180
Example
3. m∠EDF + 30 + 80 = 180 Substitution
Given: m∠F = 80 and m∠E = 30 DG bisects ∠EDF
Prove: m∠DGE = 115 4. m∠EDF = 180–110 = 70 Subtraction Property
F 5. m∠GDE = 35 Definition of angle
bisector
80° G
6. m∠GDE + m∠E + Angle Sum Theorem
m∠DGE = 180
30° 7. 35 + 30 + m∠DGE = 180 Substitution
D E
8. m∠DGE = 180–65 = 115 Subtraction Property
108