Page 120 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 120
Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors
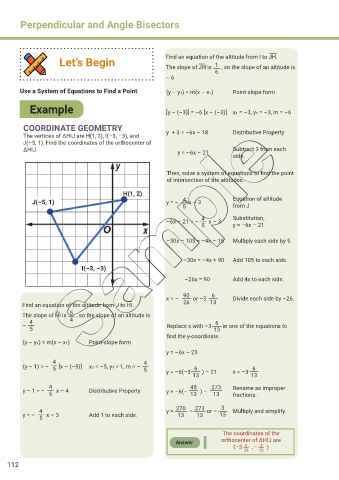
Let’s Begin Find an equation of the altitude from I to JH.
1
The slope of JH is , so the slope of an altitude is
6
– 6
Use a System of Equations to Find a Point (y – y1) = m(x – x1) Point-slope form
Example [y – (–3)] = –6 [x – (–3)] x1 = –3, y1 = –3, m = –6
COORDINATE GEOMETRY
The vertices of ΔHIJ are H(1, 2), I(–3, –3), and y + 3 = –6x – 18 Distributive Property
J(–5, 1). Find the coordinates of the orthocenter of
ΔHIJ. y = –6x – 21 Subtract 3 from each
side.
Then, solve a system of equations to find the point
of intersection of the altitudes.
H(1, 2)
4
J(–5, 1) y = – x – 3 Equation of altitude
5 from J
4
–6x – 21 = – x – 3 Substitution,
5 y = –6x – 21
–30x – 105 = –4x – 15 Multiply each side by 5.
–30x = –4x + 90 Add 105 to each side.
I(–3, –3)
–26x = 90 Add 4x to each side.
90
x = – or –3 6 Divide each side by –26.
Find an equation of the altitude from J to HI. 26 13
5
The slope of HI is , so the slope of an altitude is
4 4 6
– Replace x with –3 in one of the equations to
5 13
find the y-coordinate.
(y – y1) = m(x – x1) Point-slope form
y = –6x – 21
4 4
(y – 1) = – [x – (–5)] x1 = –5, y1 = 1, m = – 5 y = –6(–3 ) – 21 x = –3 13
6
6
5
13
4 45 273 Rename as improper
y – 1 = – x – 4 Distributive Property y = –6(– ) – 13 fractions.
5
13
273
270
4 y = – or – 3 Multiply and simplify.
y = – x – 3 Add 1 to each side. 13 13 13
5
The coordinates of the
Answer orthocenter of ΔHIJ are
6
3
(–3 ,– )
13 13
112