Page 117 - Math Course 2 (Book 2)
P. 117
Perpendicular and Angle Bisectors
Your Turn!
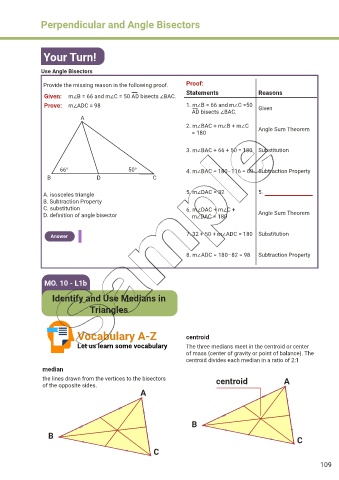
Use Angle Bisectors
Provide the missing reason in the following proof. Proof:
Statements Reasons
Given: m∠B = 66 and m∠C = 50 AD bisects ∠BAC.
Prove: m∠ADC = 98 1. m∠B = 66 and m∠C =50 Given
AD bisects ∠BAC.
A
2. m∠BAC + m∠B + m∠C Angle Sum Theorem
= 180
3. m∠BAC + 66 + 50 = 180 Substitution
66° 50° 4. m∠BAC = 180–116 = 60 Subtraction Property
B D C
A. isosceles triangle 5. m∠DAC = 32 5.
B. Subtraction Property
C. substitution 6. m∠DAC + m∠C +
D. definition of angle bisector m∠DAC = 180 Angle Sum Theorem
Answer 7. 32 + 50 + m∠ADC = 180 Substitution
8. m∠ADC = 180–82 = 98 Subtraction Property
MO. 10 - L1b
Identify and Use Medians in
Triangles
Vocabulary A-Z centroid
Let us learn some vocabulary The three medians meet in the centroid or center
of mass (center of gravity or point of balance). The
centroid divides each median in a ratio of 2:1
median
the lines drawn from the vertices to the bisectors centroid A
of the opposite sides.
A
B
B C
C
109