Page 126 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 126
Similarity of Triangles
Mo. 10
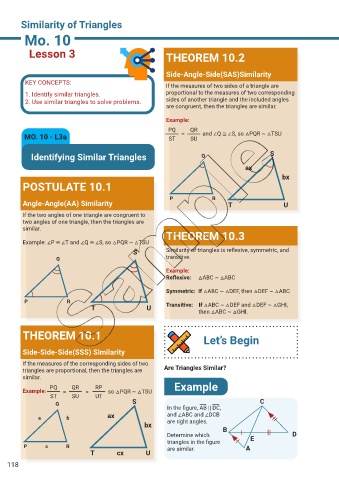
Lesson 3 THEOREM 10.2
Side-Angle-Side(SAS)Similarity
KEY CONCEPTS:
If the measures of two sides of a triangle are
1. Identify similar triangles. proportional to the measures of two corresponding
2. Use similar triangles to solve problems. sides of another triangle and the included angles
are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
Example:
PQ QR
MO. 10 - L3a ST = SU and ∠Q ≅ ∠S, so △PQR ~ △TSU
Identifying Similar Triangles Q S
ax
bx
POSTULATE 10.1
P R
Angle-Angle(AA) Similarity T U
If the two angles of one triangle are congruent to
two angles of one triangle, then the triangles are
similar.
THEOREM 10.3
Example: ∠P ≅ ∠T and ∠Q ≅ ∠S, so △PQR ~ △TSU
S Similarity of triangles is reflexive, symmetric, and
Q transitive.
Example:
Reflexive: △ABC ~ △ABC
Symmetric: If △ABC ~ △DEF, then △DEF ~ △ABC
P R
T U Transitive: If △ABC ~ △DEF and △DEF ~ △GHI,
then △ABC ~ △GHI.
THEOREM 10.1 Let’s Begin
Side-Side-Side(SSS) Similarity
If the measures of the corresponding sides of two
triangles are proportional, then the triangles are Are Triangles Similar?
similar.
PQ QR RP Example
Example: = = so △PQR ~ △TSU
ST SU UT
Q S C
In the figure, AB || DC,
a b ax and ∠ABC and ∠DCB
are right angles.
bx B
Determine which E D
triangles in the figure
P c R are similar. A
T cx U
118