Page 222 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 222
Mo6-L4a: What is The Periodic Table?
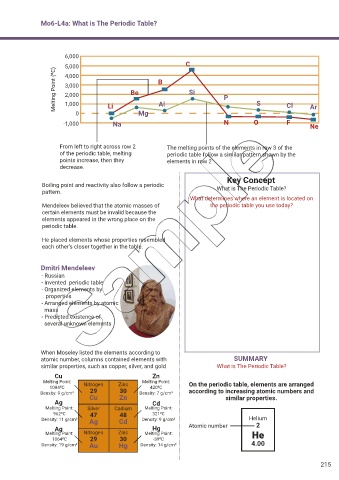
6,000
5,000 C
Melting Point (0C) 3,000 Be B Si P
4,000
2,000
1,000
0 Li Mg Al S Cl Ar
-1,000 Na N O F Ne
From left to right across row 2 The melting points of the elements in row 3 of the
of the periodic table, melting periodic table follow a similar pattern shown by the
points increase, then they elements in row 2
decrease.
Key Concept
Boiling point and reactivity also follow a periodic What is The Periodic Table?
pattern.
What determines where an element is located on
Mendeleev believed that the atomic masses of the periodic table you use today?
certain elements must be invalid because the
elements appeared in the wrong place on the
periodic table.
He placed elements whose properties resembled
each other’s closer together in the table.
Dmitri Mendeleev
- Russian
- Invented periodic table
- Organized elements by
properties
- Arranged elements by atomic
mass
- Predicted existence of
several unknown elements
When Moseley listed the elements according to
atomic number, columns contained elements with SUMMARY
similar properties, such as copper, silver, and gold What is The Periodic Table?
Cu Zn
Melting Point: Nitrogen Zinc Melting Point: On the periodic table, elements are arranged
10840C 4200C
29
Density: 9 g/cm³ Cu 30 Density: 7 g/cm³ according to increasing atomic numbers and
Zn
similar properties.
Ag Cd
Melting Point: Silver Cadium Melting Point:
9620C 47 48 3210C
Density: 11 g/cm³ Ag Cd Density: 9 g/cm³ Helium
Ag Hg Atomic number 2
Melting Point: Nitrogen Zinc Melting Point: He
10640C 29 30 -390C
Density: 19 g/cm³ Au Hg Density: 14 g/cm³ 4.00
215