Page 122 - Science Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 122
Mo11-L3a: What is Absolute-Age Dating?
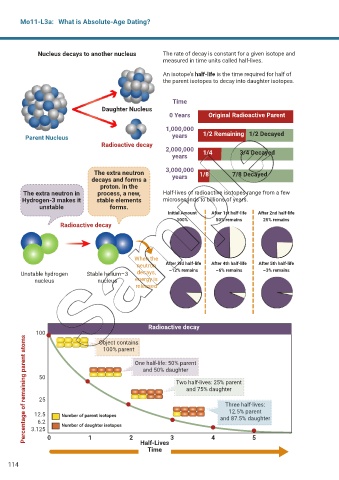
Nucleus decays to another nucleus The rate of decay is constant for a given isotope and
measured in time units called half-lives.
An isotope’s half-life is the time required for half of
the parent isotopes to decay into daughter isotopes.
Time
Daughter Nucleus
0 Years Original Radioactive Parent
1,000,000
Parent Nucleus years 1/2 Remaining 1/2 Decayed
Radioactive decay
2,000,000 1/4 3/4 Decayed
years
The extra neutron 3,000,000 1/8 7/8 Decayed
decays and forms a years
proton. In the
The extra neutron in process, a new, Half-lives of radioactive isotopes range from a few
Hydrogen-3 makes it stable elements microseconds to billions of years.
unstable forms.
Initial Amount After 1st half-life After 2nd half-life
100% 50% remains 25% remains
Radioactive decay
When the
neutron After 3rd half-life After 4th half-life After 5th half-life
Unstable hydrogen Stable helium–3 decays, ~12% remains ~6% remains ~3% remains
nucleus nucleus energy is
released
Radioactive decay
100
Percentage of remaining parent atoms
Object contains
100% parent
One half-life: 50% parent
and 50% daughter
50
Two half-lives: 25% parent
and 75% daughter
25
Three half-lives:
12.5% parent
12.5 Number of parent isotopes
6.2 and 87.5% daughter
3.125 Number of daughter isotopes
0 1 2 3 4 5
Half-Lives
Time
114