Page 125 - Science Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 125
Mo11-L3b: How to Determine Absolute Ages?
Uranium-235, or U-235, is often trapped in the For dating rocks that do not include organic material,
minerals of igneous rocks that crystallize from hot, geologists used different kinds of radioactive isotopes.
molten magma.
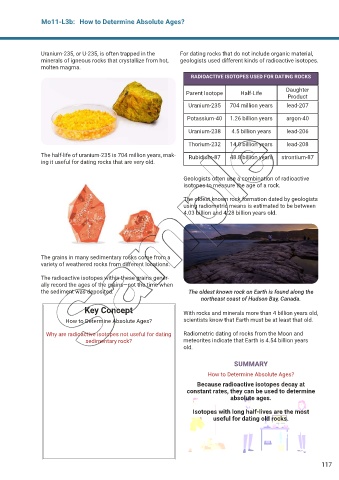
RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPES USED FOR DATING ROCKS
Daughter
Parent Isotope Half-Life
Product
Uranium-235 704 million years lead-207
Potassium-40 1.26 billion years argon-40
Uranium-238 4.5 billion years lead-206
Thorium-232 14.0 billion years lead-208
The half-life of uranium-235 is 704 million years, mak- Rubidium-87 48.8 billion years strontium-87
ing it useful for dating rocks that are very old.
Geologists often use a combination of radioactive
isotopes to measure the age of a rock.
The oldest known rock formation dated by geologists
using radiometric means is estimated to be between
4.03 billion and 4.28 billion years old.
The grains in many sedimentary rocks come from a
variety of weathered rocks from different locations.
The radioactive isotopes within these grains gener-
ally record the ages of the grains—not the time when
the sediment was deposited. The oldest known rock on Earth is found along the
northeast coast of Hudson Bay, Canada.
Key Concept With rocks and minerals more than 4 billion years old,
How to Determine Absolute Ages? scientists know that Earth must be at least that old.
Why are radioactive isotopes not useful for dating Radiometric dating of rocks from the Moon and
sedimentary rock? meteorites indicate that Earth is 4.54 billion years
old.
SUMMARY
How to Determine Absolute Ages?
Because radioactive isotopes decay at
constant rates, they can be used to determine
absolute ages.
Isotopes with long half-lives are the most
useful for dating old rocks.
117