Page 120 - Science Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 120
Absolute-Age Dating Mo11-L3a: What is Absolute-Age Dating?
Lesson 3
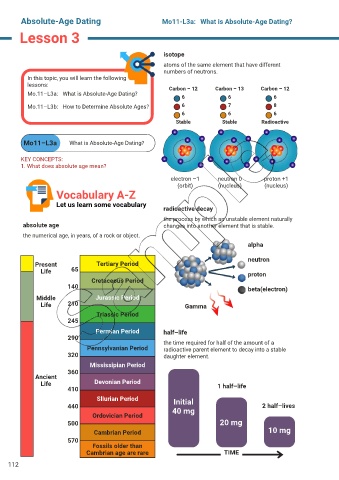
isotope
atoms of the same element that have different
numbers of neutrons.
In this topic, you will learn the following
lessons:
Carbon – 12 Carbon – 13 Carbon – 12
Mo.11–L3a: What is Absolute-Age Dating?
6 6 6
Mo.11–L3b: How to Determine Absolute Ages? 6 7 8
6 6 6
Stable Stable Radioactive
Mo11–L3a What is Absolute-Age Dating?
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. What does absolute age mean?
electron –1 neutron 0 proton +1
(orbit) (nucleus) (nucleus)
Vocabulary A-Z
Let us learn some vocabulary
radioactive decay
the process by which an unstable element naturally
absolute age changes into another element that is stable.
the numerical age, in years, of a rock or object.
alpha
neutron
Present Tertiary Period
Life 65 proton
Cretaceous Period
140 beta(electron)
Middle Jurassic Period
Life 210 Gamma
Triassic Period
245
Permian Period half–life
290
the time required for half of the amount of a
Pennsylvanian Period radioactive parent element to decay into a stable
320 daughter element.
Mississipian Period
360
Ancient
Life Devonian Period 1 half–life
410
Sllurian Period Initial
440 40 mg 2 half–lives
Ordovician Period
500 20 mg
Cambrian Period 10 mg
570
Fossils older than
Cambrian age are rare TIME
112